Online Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide
Do you know who Chandler Bolt is?
If you’re an online marketing nerd like me, you probably do.
But, if you’re part of the other 99.9% of the world who isn’t super excited about this “Internet marketing stuff,” you’ve probably never heard of this man.
So, what is he doing with this headline on Business Insider?
How did he get on there?
Is he rich or something? Yes, he is indeed.
That’s part of the beauty of online marketing.
This 21-year-old kid has made hundreds of thousands of dollars from his kitchen table.
No need for fame, magazine interviews, talk show visits, or acting classes (you know, to act in a blockbuster movie).
You have no clue who Chandler Bolt is. But he has made tons of money, and he’s also helping others do the same.
His company, Self-Publishing School, helps people publish books on Amazon and make a living from it.
If you’re an introvert, that’s a cause to celebrate!
Fewer than 20 years ago, extroverts had a way better chance of becoming rich and successful.
Why? It involved a ton of networking.
You had to hire employees and build a huge company. Or, for a career in arts, music, movies, etc., you had to get every person in your industry to know you.
While connections are still a huge deal, today you can get them right from your couch (or from your living room floor in my case).
As a single individual, you can build a huge business from the comfort of your home after work, during your afternoons, and on your weekends.
I don’t think that I’m being overly dramatic when I say that online marketing is your shot at the life of your dreams.
Trust me — I would know.
I want you to have as much fun at work as these guys and I do. So, today I’ll introduce you to this world with my online marketing guide.
Note: Even if you’re deep down the rabbit hole already, you can still learn a ton of new things from the following examples.
If you’re interested in a particular topic, feel free to jump ahead:
- Definition
- Overview
- SEO – Search Engine Optimization
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- SEM – Search Engine Marketing
- Content marketing
- Why content marketing?
- Social media marketing
- Pay-per-click advertising
- Everything that you need to know about Google AdWords
- Affiliate marketing
- Email marketing
Definition
If you’ve read my previous guide on digital marketing, you already know that it’s different.
Not every digital marketing campaign is automatically an online marketing effort.
According to TNMedia, online marketing is “…any tool, strategy or method of getting the company name out to the public. The advertisements can take many different forms and some strategies focus on subtle messages rather than clear-cut advertisements.”
Want the drop-dead simple version of it?
Online marketing is any effort to spread the word about your company that uses the Internet to reach people.
Basically, it’s anything that you do online to get more eyeballs on you, grab people’s attention, and hopefully, at some point, get them to buy from you.
There are seven major sub-categories of online marketing that I want to cover in this guide.
Overview
We’ve already talked about search engine optimization (SEO), and I showed you all of the important aspects of it that you have to get right.
Next to SEO, there’s search engine marketing (SEM), which is simply the paid version of SEO.
Marketers pay Google to display ads in their search results in the hopes that they will drive traffic (especially interested people, or leads) to their product landing pages.
Then there’s content marketing. This is where marketers try to create valuable media and content to distribute to potential future customers. This is the good guy version of online marketing where you mostly try to guilt people into buying.
Of course, you already know social media marketing, which is where you use one or several social media channels to engage with customers, build relationships, and then send them to your products and services.
Pay per click advertising (or PPC) is similar to search engine marketing, but it isn’t limited to Google and its competitors. Most social media networks let you create ads that integrate naturally into their feeds, allowing you to pay for clicks to your website.
Affiliate marketing is a kind of referral marketing where you share profits with fellow marketers in exchange for promoting each other’s products.
And finally, there’s email marketing, which some already consider old-school. But it’s still one of the most effective channels. Once your customers have given you permission to contact them, you can email them at any time, providing value and asking them to buy when the time is right.
You can already guess how big online marketing really is. You know how huge of a space each of these individual categories fill.
I mean, just think about how many social media platforms you can name off the top of your head:
Facebook, Pinterest, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, Tumblr, Google+, YouTube, Periscope, LinkedIn, Reddit, StumbleUpon…
OK, you get the point.
I want to give you a good grip on all of these categories just like in our beginner’s guide, yet not drown you in the vast information that’s out there.
That’s why I’ll give you one example in each category of someone who absolutely crushes it in their niche along with some great points to help you get started.
Ready. Set. Go!
SEO – Search Engine Optimization
It goes without saying that I think Quick Sprout is one of the best sites when it comes to SEO (we’re kind of a big deal, I think).
Our Advanced Guide to SEO alone has gotten thousands of shares.
But, instead of spending an entire category bragging, I want to point you to someone who is a true search engine marketing ninja who has worked for us at Quick Sprout for quite some time.
I want to point him out not only because he has all of the SEO skills you need up his sleeve, but also because he is super underrated.
Every time I read an article like“15 SEO Gurus That You Should Know for 2015,” I’m shocked that he’s not on there.
Brian Dean, aka Backlinko, might be flying under the radar. But when you start Googling around and learning SEO, you’re bound to bump into him.
He outranks huge sites like Wikipedia, Forbes, and Copyblogger, and he completely dominates the SEO space with his super long case studies that provide actionable, step-by-step instructions for upping your SEO game.
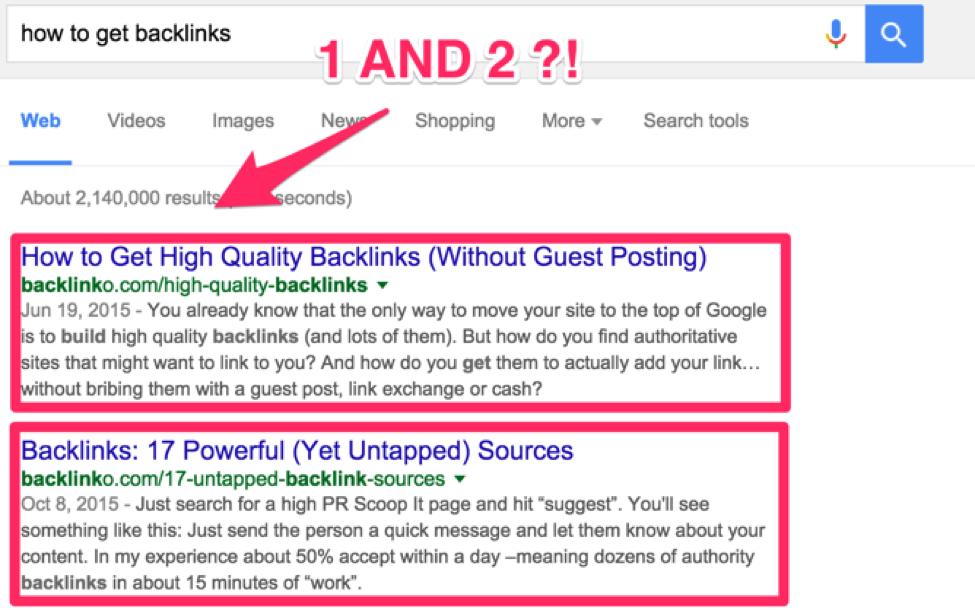
Backlinko ranks #1 AND #2 for “how to get backlinks.”
What’s great about his blog is that instead of just rounding up SEO news like Search Engine Land and others do, he actually shows you how to implement good SEO techniques that work.
As I outlined in one of the previous guides in this series, SEO is the process of optimizing your online content so that a search engine likes to show it as a top result for searches of a certain keyword.
Brian is one of the best sources on the web for you to learn how to do search engine marketing right.
For example, Brian recently published an article called “How to get backlinks with guestographics.”
There, he does two things.
1. He shows you the results that prove thatthe strategy works.
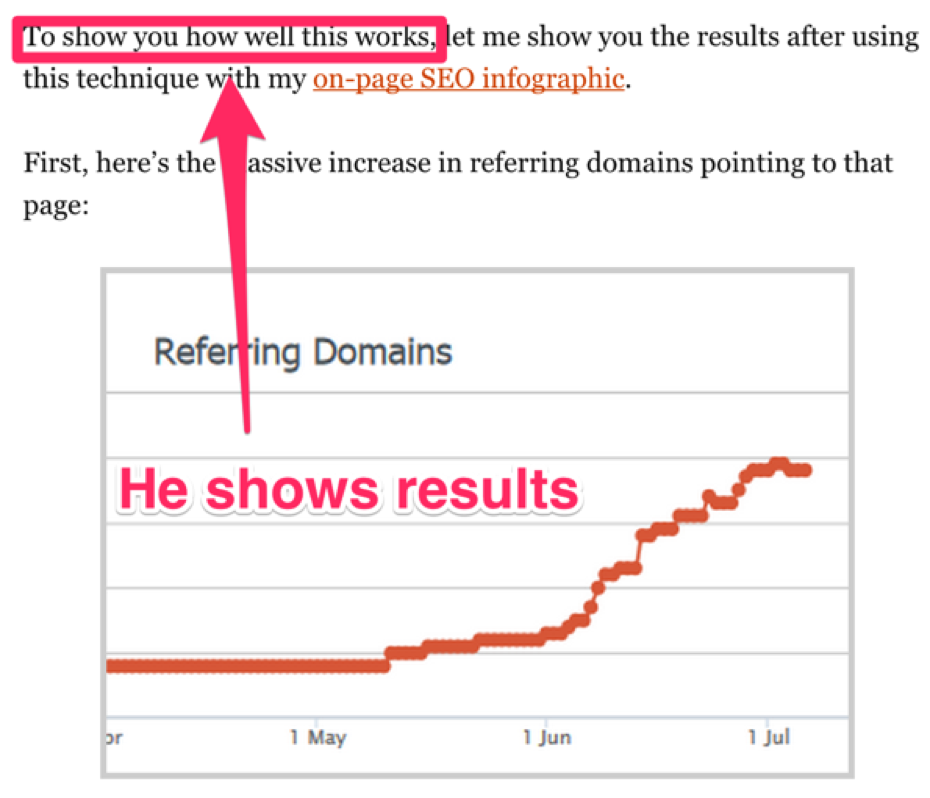
2. He gives you detailed steps that you can follow to execute it.
As a case study, he talks about someone who he’s helped pull off this strategy in their niche.
You see the results, and then you can just scroll down and follow along as you read. In this case, the steps are:
- Step 1: Publish an Awesome Infographic
- Step 2: Simple (But Effective) Link Prospecting
- Step 3: Show Them Your Infographic
- Step 4: Bribe Your Prospects With Free Content
- Step 5: Get Your Contextual Links
That’s easy to follow, right? So, what’s the catch?
It’s hard to execute. It takes time.
And that’s the reason that not many people do it. Be one of the few who does and you’ll get the results.
Just check out this backlink that we got to a Quick Sprout infographic:

Do you want more proof?
Go through the entire Backlinko blog. You’ll find fewer than 40 posts over the last several years.
If Brian’s SEO didn’t work, then he would never have been able to grow Backlinko to 100,000+ monthly readers, 100,000 email subscribers, and such a massive SEO brand with fewer than 40 blog posts.
The following three blog posts are the best ones to help you get started:
- How to rank for any keyword
- Link Building: The Definitive Guide
- Google’s 200 Ranking Factors: The Complete List
Within search engine optimization, there are two big sectors to be aware of:
On-page and off-page SEO. Let’s dive into each.
On-Page SEO
Over the past few years, Google has made numerous updates to their algorithms.
Data tells us that Google makes up to 600 changes to their algorithm every single year.
It’s almost impossible to keep up with Google’s rapid pace and changing user behavior.
But one thing that’s remained relatively constant is conducting on-page SEO.
Most on-page activities for SEO aren’t linked to direct ranking factors, but rather to indirect factors like click-through rate and time on site.
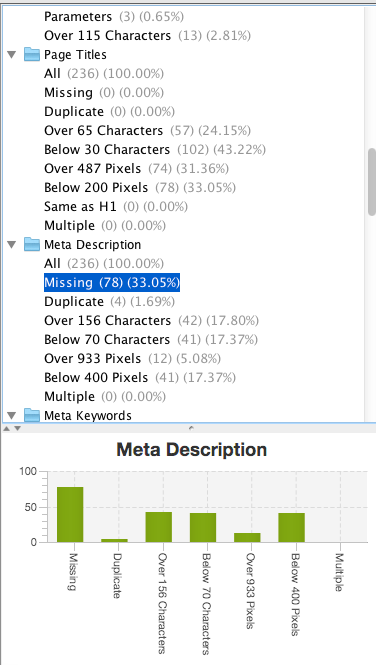
For example, an on-page SEO task that’s common is to optimize your meta description and title tag:
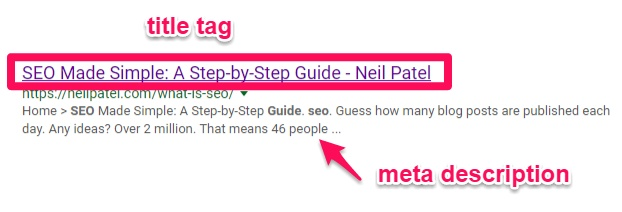
Your title tag and meta description are what shows up on a given Google search result. For example, if someone searches for “SEO Tips,” my post will show up with the headline and description that I’ve personally customized.
While placing keywords in the title and description can help users navigate the content faster (as seen by the bolded text), it doesn’t directly increase rankings.
So simply stuffing keywords in your meta and title tags isn’t an option.
But they do contribute to click-through rate. When your title tags and meta descriptions are more compelling or related to the topic that someone is searching for, you can expect higher click-through rates.
And the higher the CTR, the higher the chance of ranking better.
Google is all about providing the best user experience possible. So if Google notices that your post that ranks at #10 is getting a higher CTR than the post above you, they will move your content up.
On-page SEO consists of a few major elements to be aware of:
- Crawl errors
- Keyword research
- Page optimization
- Speed
In this section, I’ll walk you through how you can improve each of these elements to get your on-page SEO on the right track.
Crawl errors
Crawl errors can be anything from a 404 error (broken link) to duplicate content. And all of these issues can plague your website with:
- Slow speeds
- Impacted rankings
- Penalties from Google
- Increased risk of users leaving your site (bouncing)
If you’ve ever seen this on your site, it’s a broken link error that can cause major problems:

For example, 404 errors can impact your traffic heavily if another external source is linking to them.
If you’ve gotten your content featured on another site, but the link is broken, you’re losing out on tons of traffic.
One of the fastest tools to fix crawl errors that could be harming your site is Screaming Frog.
It’s a technical SEO tool that can scan your website for free, telling you detailed information on what you need to fix and how to do it:
When scanning your site, be sure to look for common problem areas like:
- Duplicate or missing content
- 404 errors
These issues are all too common on the majority of sites.
Keyword research
Keyword research is a fundamental process in any online marketing game plan for SEO.
Keywords are what you search in a search engine to find the content you are looking for.
For example, type “SEO Guide” into Google — that would be a keyword. And pages can target these keywords to compete in the rankings.
There are a few types of keywords to be aware of before conducting a basic keyword research strategy. There are two major kinds:
- Long-tail keywords: Long-tail keywords are longer keywords made up of 3-5+ words. They are often easier to target due to specificity, less traffic, and less competition.
- Head keywords: Head or short-tail keywords are one-word or two-word keywords that are more general. For example, “basketball shoes” would be a competitive head keyword.
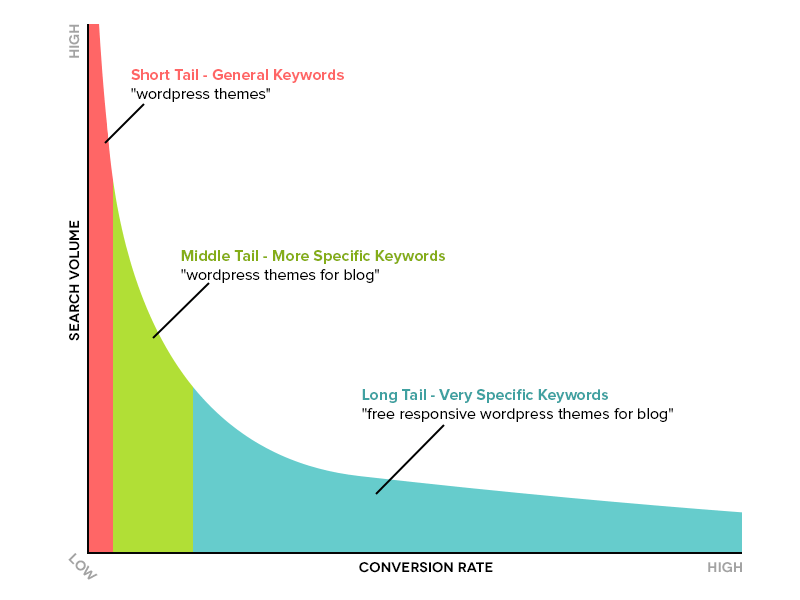
A good SEO strategy will target a mixture of both of these kinds of terms.
Short-tail keywords will be much more competitive because they are more general (and therefore have a higher volume).
On the other hand, long-tail keywords will get you less traffic but will convert better:
To conduct keyword research, all you need to do is head to a keyword tool like Moz or the AdWords Keyword Planner.
Simply start by entering the basic topic that you want to cover for your next post or page:
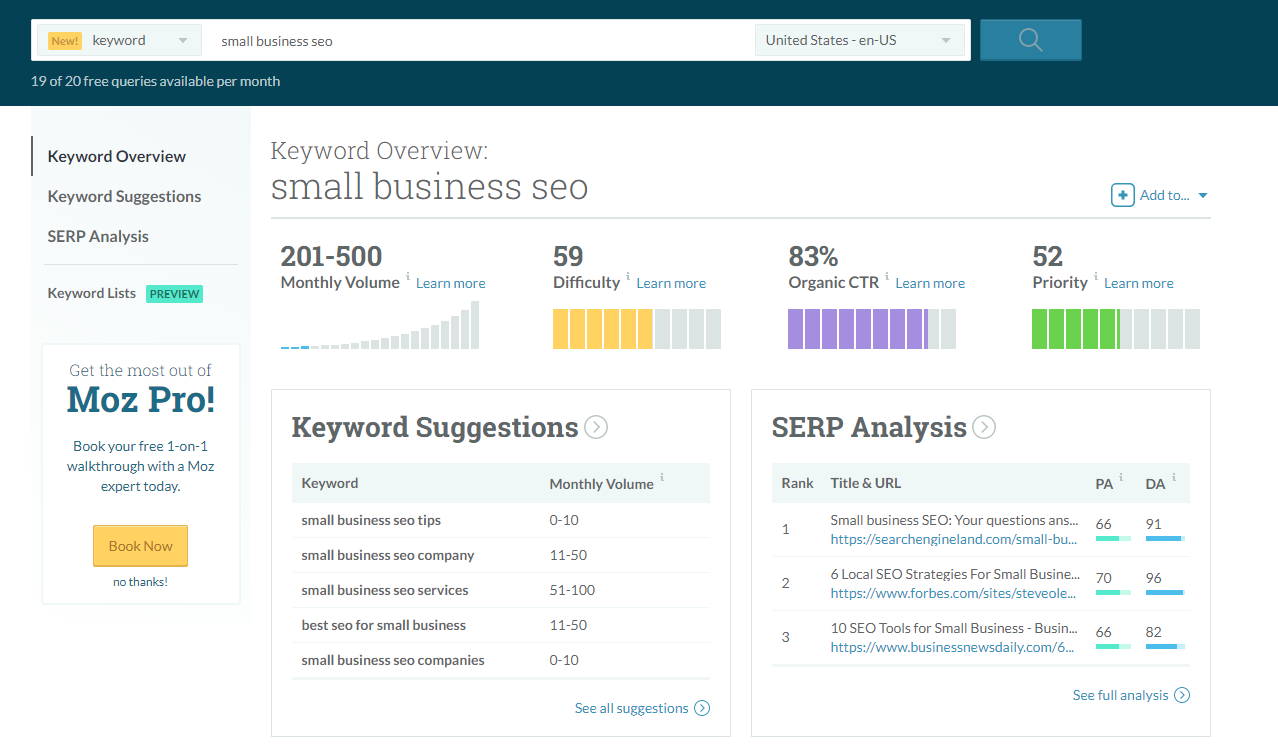
Searching for your basic keyword will give you a list of metrics telling you the volume (how many searches per month), difficulty (competition ranking for it), and the number of clicks that come from organic search.
Lastly, it will also give you keyword suggestions.
Generally speaking, when looking to target keywords for your next blog post, you want to find long-tail terms with higher volumes and lower difficulty scores.
Then, you can take that keyword and follow the next steps under page optimization!
Page optimization
Page optimization is a critical step in the process of SEO. Page optimization involves doing a few basic tasks to optimize your page for specific keywords and for search engines.
Remember: You’re writing content and optimizing pages for both the user and the search engine.
Everything from URLs to internal links can have an impact on your page performance.
This on-page SEO checklist from Backlinko is one of my favorite ways to stay on top of every new blog post that I write:
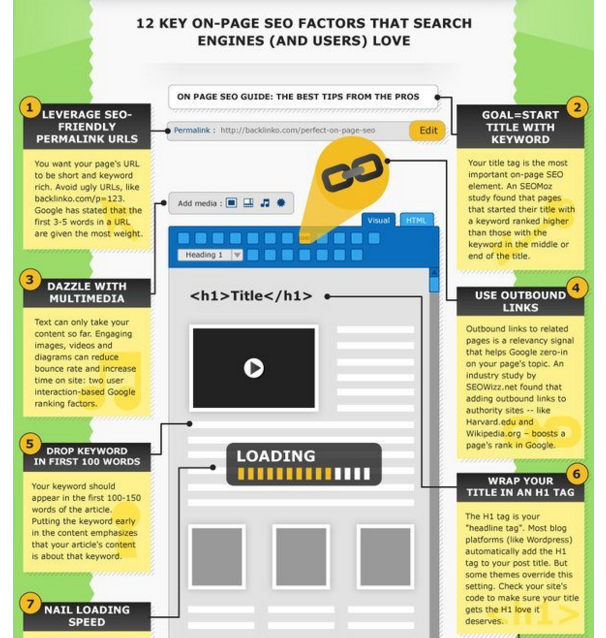
All of these factors help you to both add context to the page for Google and structure it in a friendly way for the user.
For example, when you search for an article on Google, you expect to get something similar to your search:
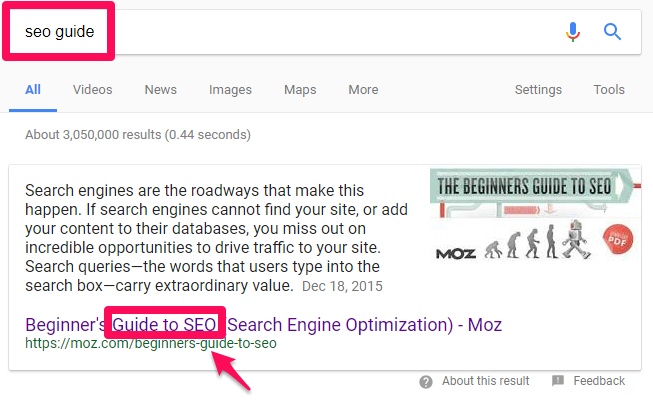
Everything from the permalink (URL) to the title and structure of your post (h1 and h2 headings) makes a difference in how Google scans your content and how user-friendly it is.
The better on-page optimization you have, the longer users will stay around to consume your content.
Plus, optimizing things like internal links (where you link to another article on your site from a new post) will help you drive users throughout your entire site.
Always be sure to follow the on-page SEO cheat sheet above when you write new blog posts.
Improve your page speed
One of the biggest factors for success is improving the speed at which your page loads.
When it comes to SEO, you want your content to load fast. Google prefers websites that load fast as well.
Studies have shown time and time again that top-ranking sites are faster than their lower-ranking competitors:
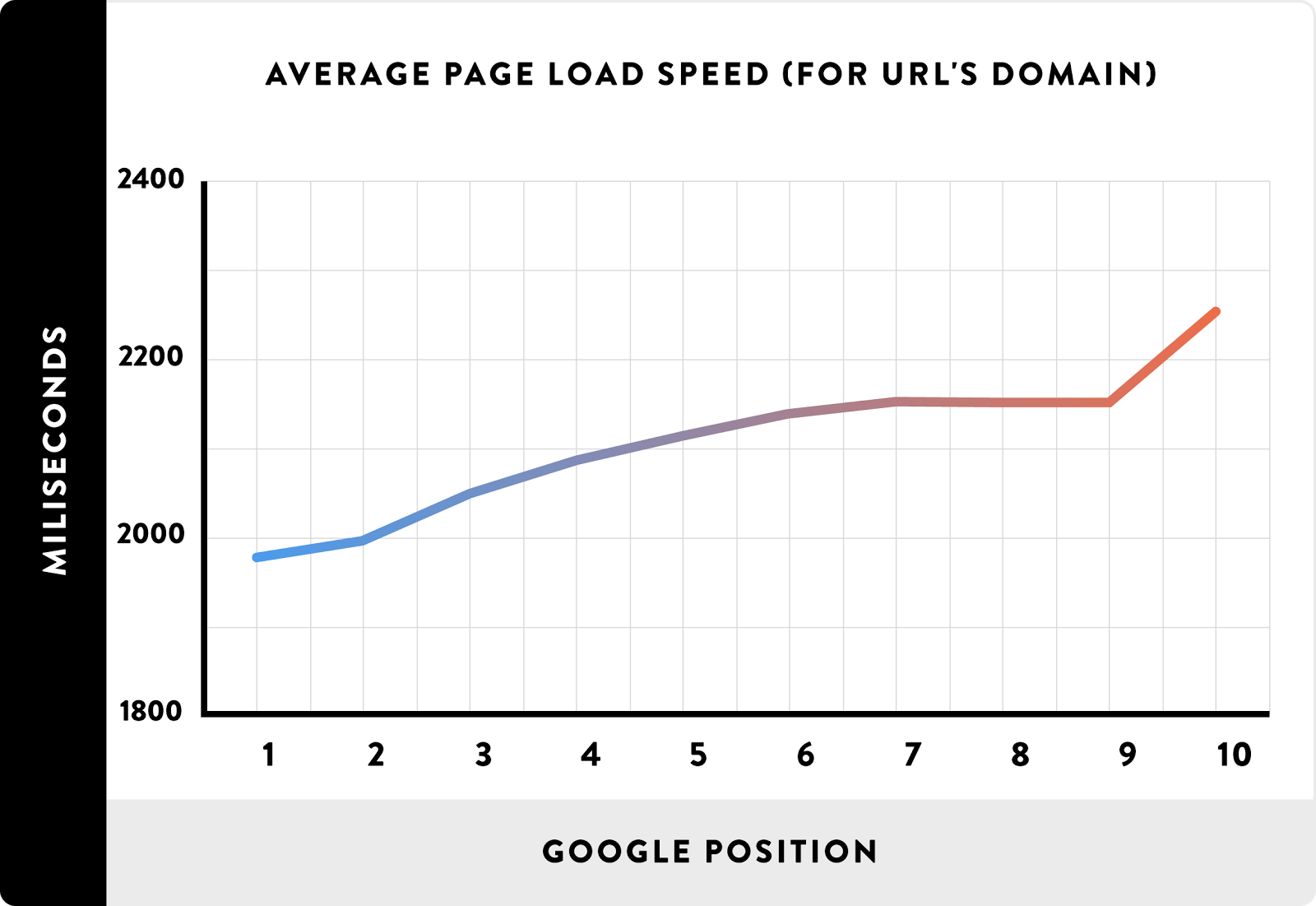
According to their latest reports, as page load times increase by just a few seconds, the likelihood that someone will leave your site increases dramatically.
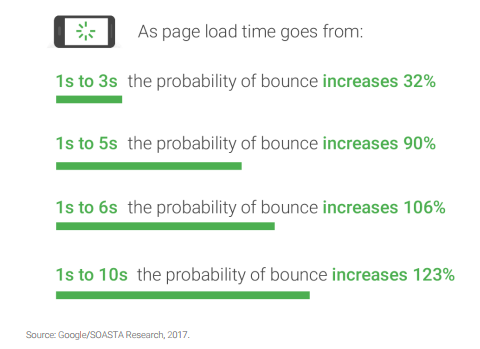
If your site loads in ten seconds, you can expect users to run for the hills.
Google’s current standards state that best practices are three seconds or below. Yet the majority of businesses in every industry are still too slow:
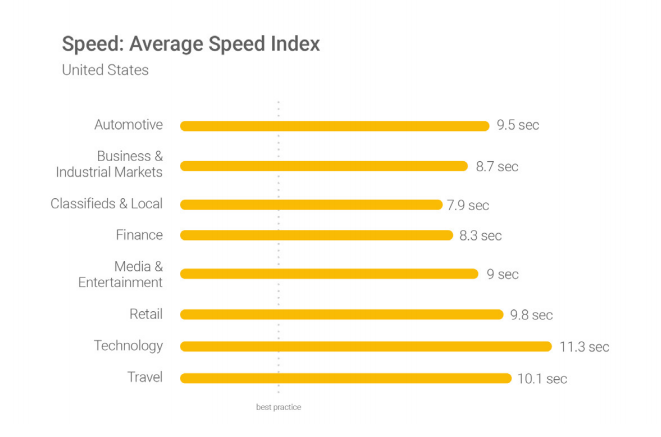
Thankfully, Google offers free tools like Test My Site and Pagespeed Insights. Each of these can help you improve your site speed dramatically.
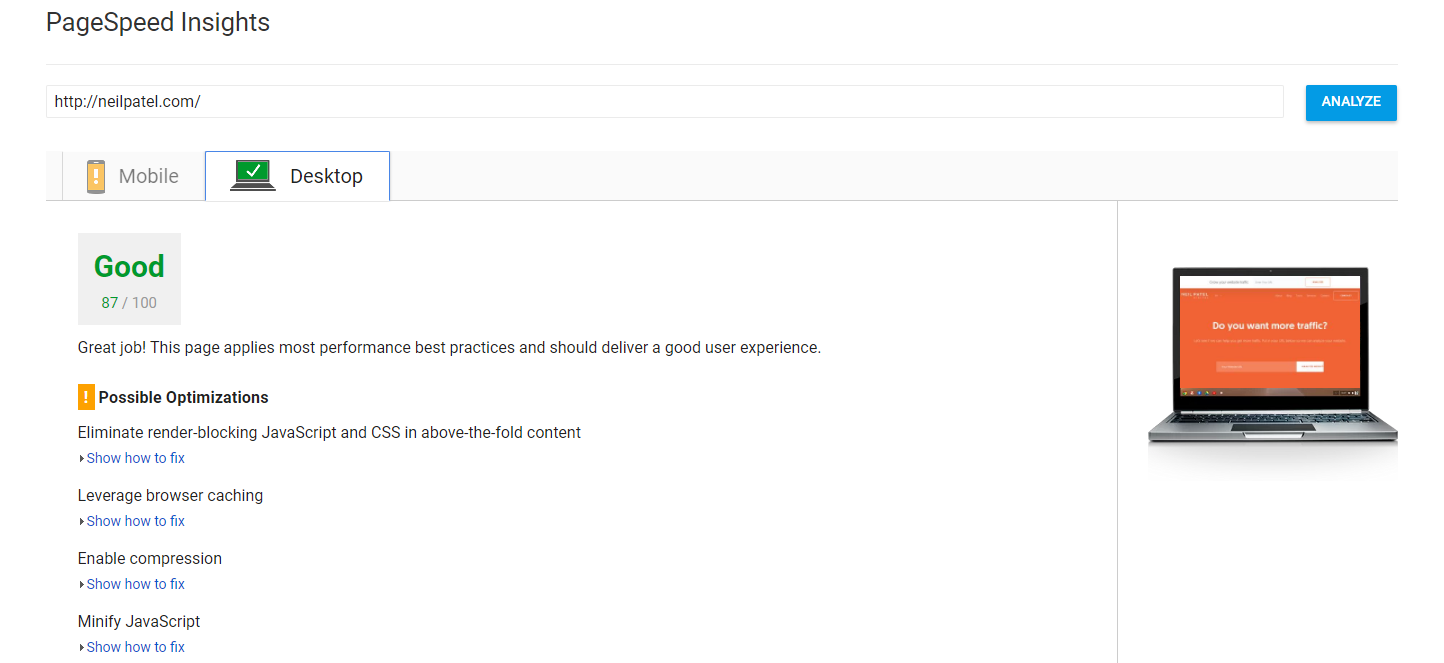
When you improve your site speeds, you can expect users to stay around on your site, reducing bounce rates that can negatively impact your organic rankings.
Always continue to test your site speed and improve where you can. These tools will help you fix any lingering problems by offering detailed, step-by-step solutions under each problem area.
Off-Page SEO
What’s off-page SEO? It’s simply the opposite of on-page SEO.
That means that it’s all of the factors and activities that you can do (off-page) to raise the ranking of your site on search engines.
There are a few major ways that off-page SEO comes into play. Everything from link building to social promotion and content syndication can improve your off-page SEO.
Even things like guest blogging or writing a promotional piece on another site can result in a link (i.e., off-page SEO).
Here are a few ways to rank higher with off-page SEO.
Link building is critical
Link building is the most important factor in any off-page SEO strategy. According to a video from 2016 featuring Andrey Lipattsev, a Search Quality Senior Strategist at Google, links and content were tied as the top two ranking factors.
Google confirmed this official video. Links are one of the biggest factors when it comes to ranking in a given search result.
When Brian Dean of Backlinko tested this with his own study, he found that the sites that rank number one dominate the competition in terms of backlinks.
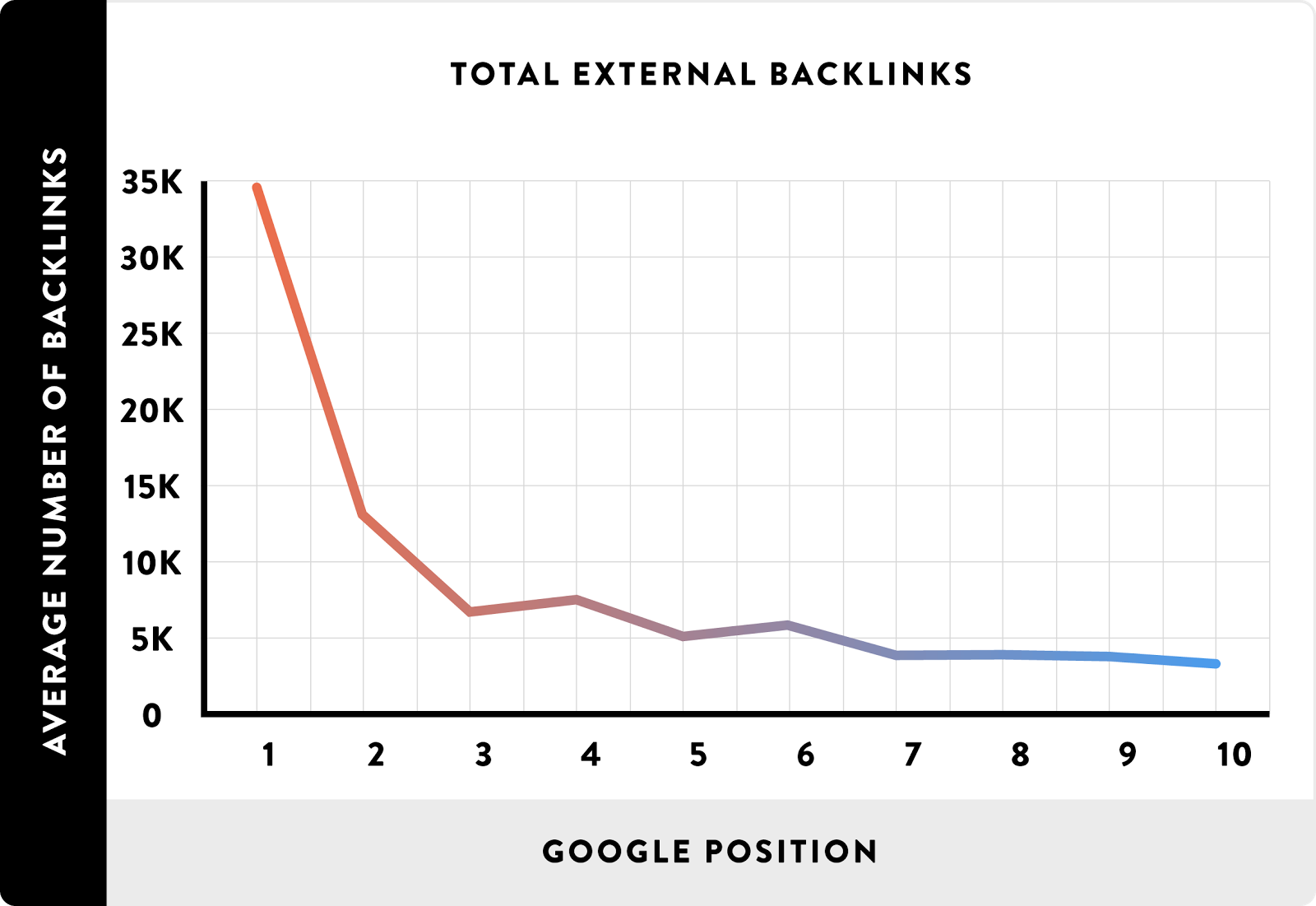
The more links you have back to your site from other sites, the stronger authority you have in the eyes of Google. It means that your content is relevant.
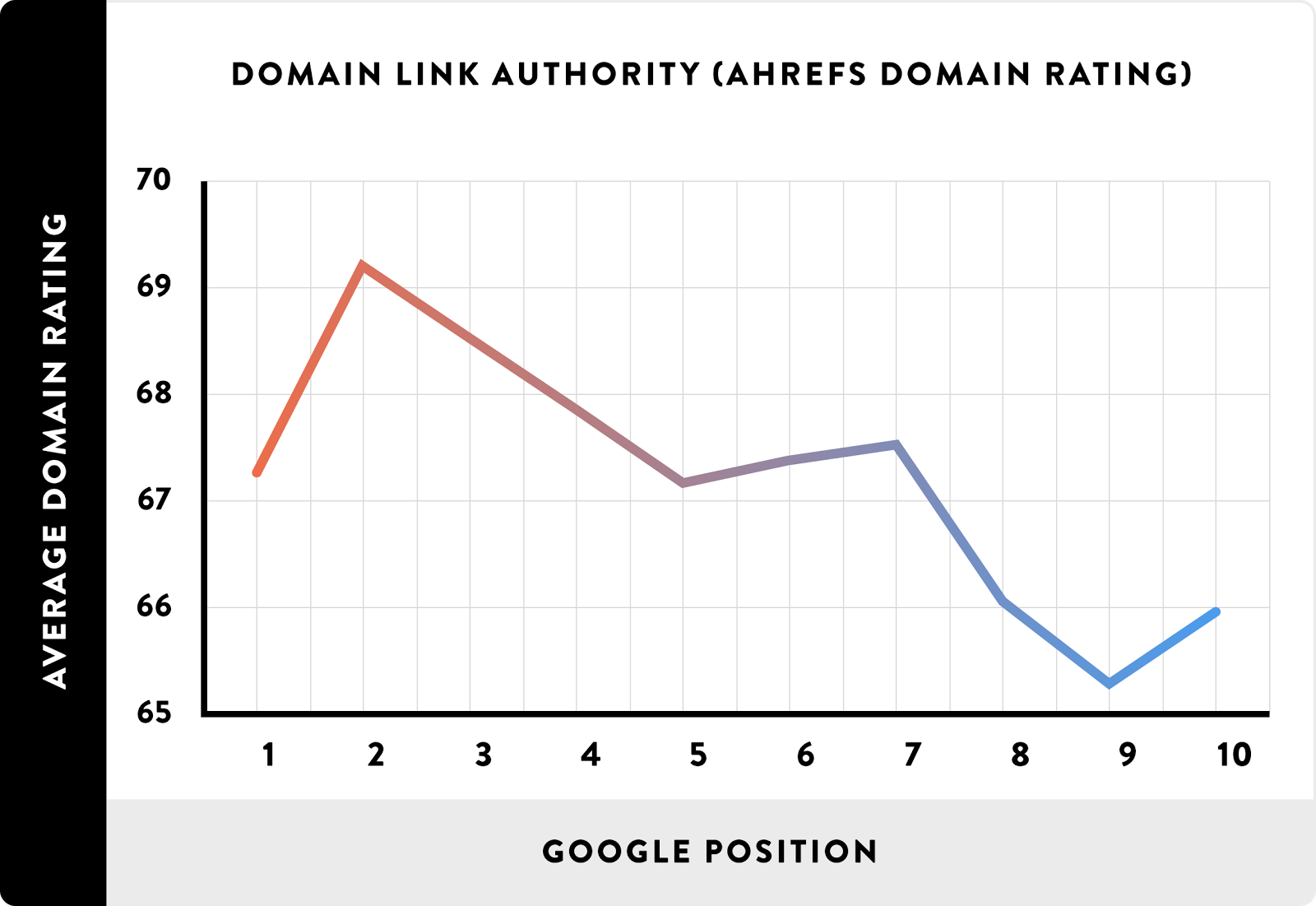
But not just any links will do the trick. That same study found that top-ranking sites with backlinks had links from hundreds of different sites:
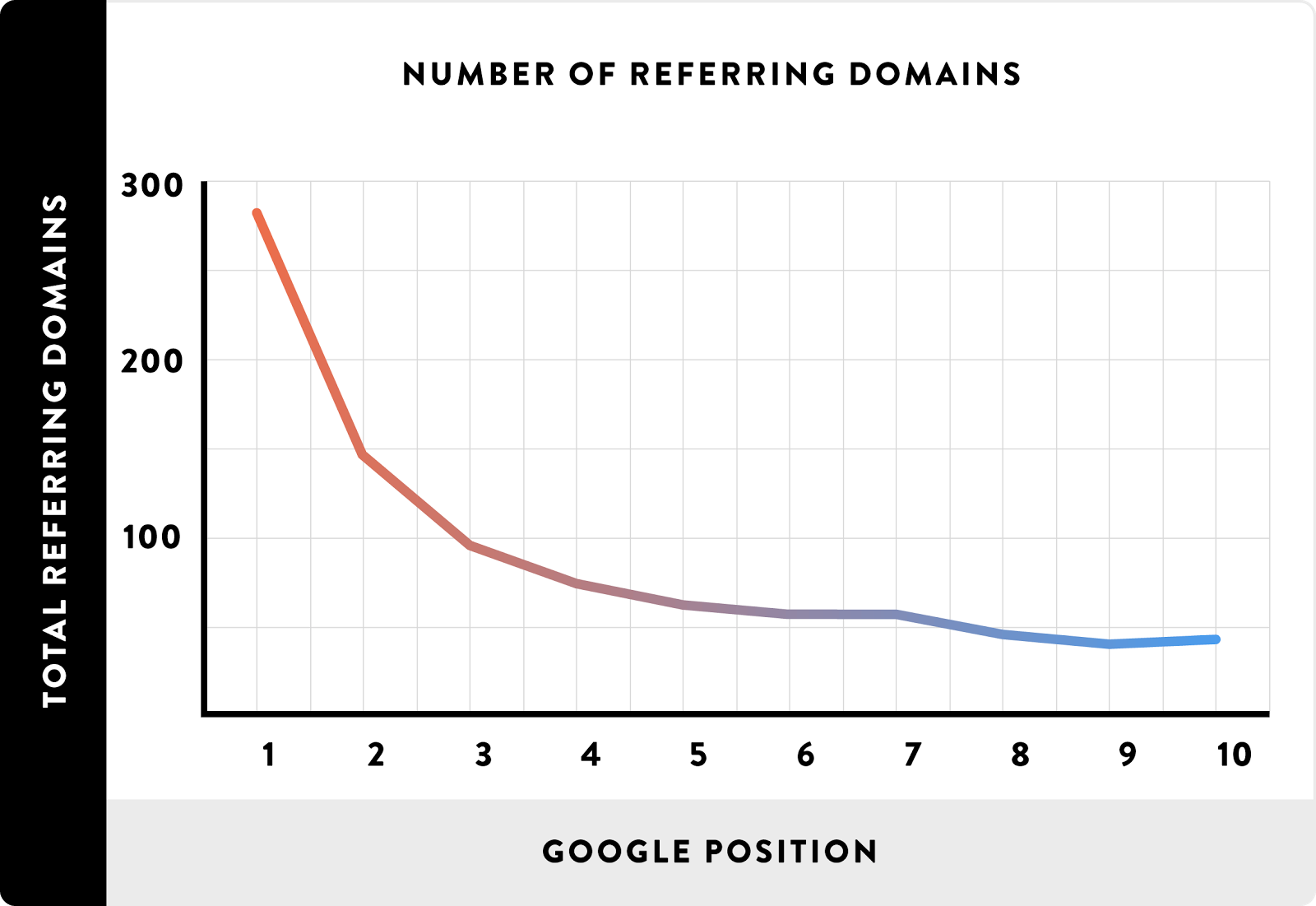
And the vast majority of those links were from the highest-ranking authorities in their space:
Link building is tough, but it’s necessary to compete with SEO for online marketing.
Ranking higher with links involves everything from your total number of links to the quality of those links and the diversity of the sources.
When it comes to getting links, you need great content. The majority of content ranking #1 on Google is stellar.
And that’s why they have thousands of links. The content is nearly unmatched!
In Moz’s book “How to Rank,” they explain the 90/10 rule of link building:
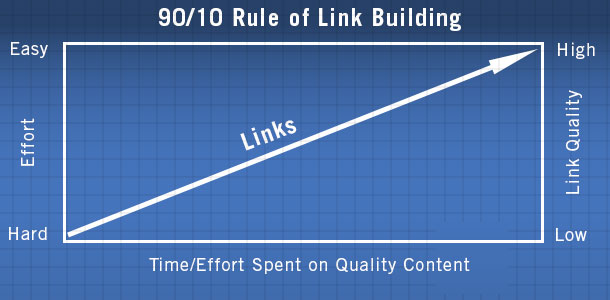
That means that you should spend 90% of your time creating amazing content and dedicate 10% of your time to link building.
Without great content, you won’t get the links you need to bring in more traffic and drive sales.
One of my favorite ways to build backlinks fast is by mentioning other influencers in my content. This adds great value to your content while also mentioning and giving praise to others.
And as we all know, humans love it when people lift their egos. It’s a great feeling to get compliments and praise for your knowledge in a space.
By tapping into that and getting value and input from influencers, you can easily drive backlinks.
For example, Shopify recently mentioned me in this post:

I was a featured influencer on the post because I gave them tons of input. So in this post, I received a backlink to my site in exchange for my time and effort.

But I have also linked to this post multiple times since simply because it mentions me.
Mentioning influencers is a great way to get them to share your post!
Do you want to build backlinks fast? Here are a few key resources:
- How to Build High-Quality Backlinks in a Scalable Way
- 9 Link Building Resources That’ll Increase Your Search Rankings
- 13 Efficient Link Building Strategies for Busy Marketers
- The Advanced Guide to Link Building
Social sharing
Social publishing is a great way to indirectly contribute to your off-page SEO strategy. While it’s not a direct ranking factor, it’s an off-page tactic that can lead to more backlinks.
Sharing your latest post on social media helps to spread it to new audiences. The more users you attract, the more brand awareness you get, and hopefully, the more links you can get as well.
Try using a tool like Buffer to schedule your content in advance:
Using platforms like LinkedIn is one of my favorite ways to conduct off-page SEO with social media as well.
Beyond simply sharing your latest posts, a great strategy is to write articles on LinkedIn, directing traffic back to your site.
Let me show you an example of a recent article I posted on LinkedIn:
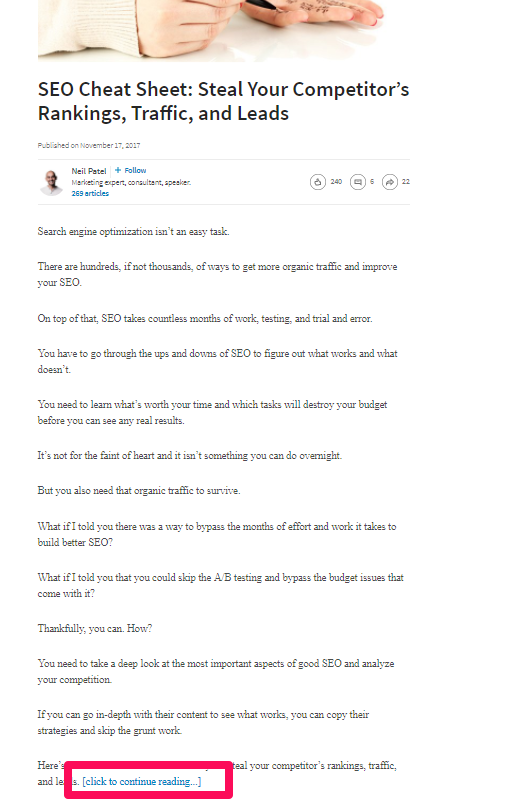
LinkedIn articles are much different than simply pasting your blog post into the status update bar.
These articles are published content that alerts all of your connections each time a new article goes live. That means that each person who follows you will get a notification rather than having to stumble across it while scrolling through a timeline.
My favorite strategy for LinkedIn articles is to copy the introduction paragraph of my latest blog post and end it with [click to continue reading…].
I then hyperlink that phrase back to my full blog post on my site, driving tons of traffic and engagement!
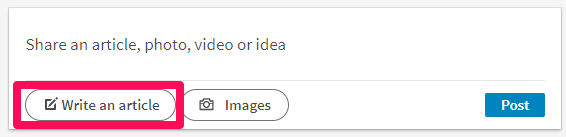
To get started with this off-page SEO tactic, head to LinkedIn and select “Write an article”:
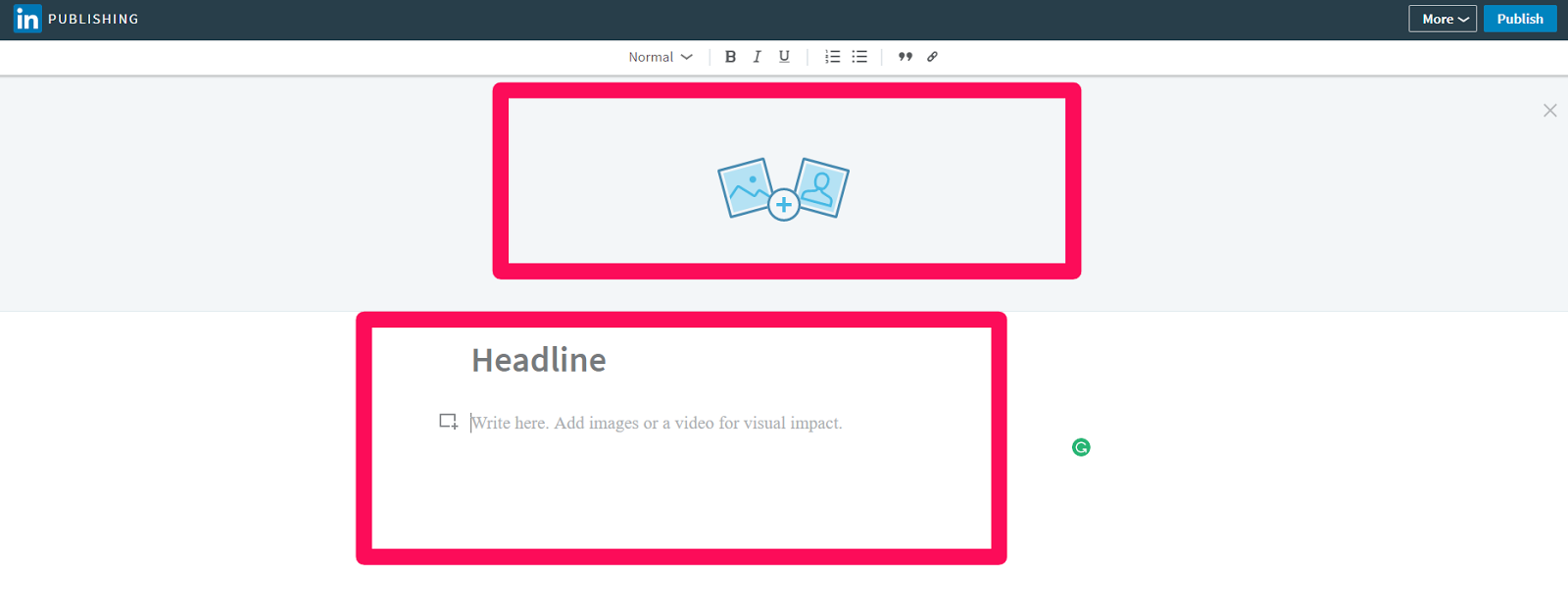
Next, add your featured image from your blog post and copy and paste the headline and intro paragraph:
Add your “click to continue reading” tag at the end and watch your traffic and links skyrocket.
SEM – Search Engine Marketing
Search engine marketing is the paid cousin of SEO.
Instead of optimizing your content and promoting it a lot to eventually show up as a top result for organic search engine results (which can often take a few months to happen even if you do it right), you can pay your way to the top.
And since it’s the first thing searchers see on the page, you’ll likely get a lot of hits to your site. But you also pay for each and every one.
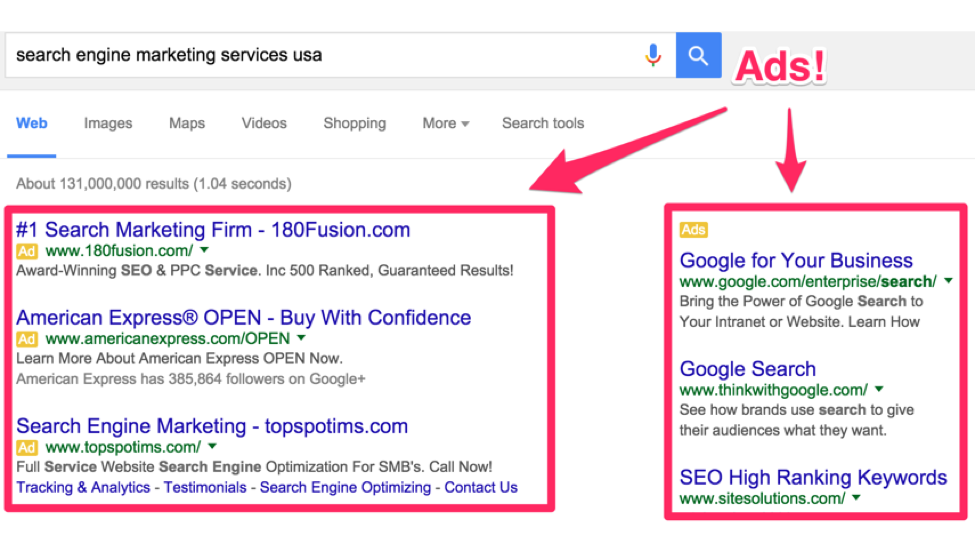
Depending on what keyword you want to show up for, you pay different prices.
The keywords that people search a lot for are more competitive and are therefore more expensive.
Some keywords can cost several hundred dollars per click.
Some cost over $600 for a single click!
So, while it is a great strategy, it only works if you can immediately recoup your advertising costs.
Companies easily blow tens of thousands of dollars on Google AdWords campaigns, failing to make sure that they get their money’s worth.
To win with SEM, you have to offer a paid product or service.
When you’re still in the phase of producing free content to build an audience, don’t waste your time with SEM. You’ll run out of money faster than you can spell S-E-M.
Thankfully, avoiding the mistake of paying for worthless clicks is not as hard as you might think.
By setting up conversion goals inside of your campaign, you can track exactly who made a purchase from your ads, and you’ll know exactly how much money you spent and how much you made at any time.
Google has published several case studies of customers who spent hundreds of thousands of dollars on Google AdWords and yielded even better returns.
Their ROI (return on investment) is often way higher than any stock or real estate investment could be, creating 5x, 10x, and even 20x the ad spend in conversions. That’s Internet marketing at it’s finest!
A great source to get started with Google AdWords, whether you’re an established business or a solo entrepreneur sitting on his couch, is Jerry Banfield.
Jerry made a living as a full-time instructor on Udemy, often generating $30,000 or more in monthly income.
He was able to scale up his sales this much because of Google AdWords.
Prior to his solopreneur career, Jerry ran a one-man ad agency, helping businesses with their SEM. Once he had a few courses to sell, he went on to transfer his SEM skills to his own business.
Look at the kind of results he creates:
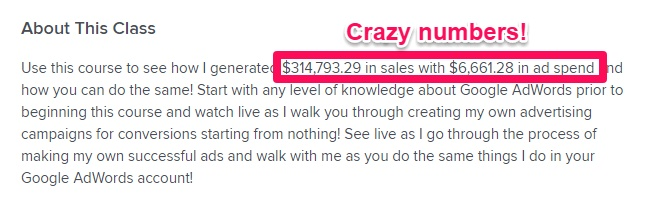
That’s an ROI of 4700%! That’s how powerful Google AdWords can be.
Even better, Jerry teaches everything he knows, and most of his lessons are free. By far, the best place to start learning Google AdWords is his free course on YouTube.
It walks you through everything that you need to know to set up your first campaign from scratch, and it’s over 3 hours long.
The lessons in this video alone are more than enough to help you get started. And, once you’re ready to kick it up a notch, you can just get his Udemy course for over 9 hours of videos, detailed tutorials, and guides.
Content marketing
Jon Morrow is a master content crafter. After getting annoyed by how great content often suffers from little traffic and exposure, he set out to help people change that.
His blog, Boost Blog Traffic, boasts over 500,000 monthly readers.
As I taught you in the previous guide, content marketing is all about providing timely and relevant value to your audience.
The first step to doing that is knowing your stuff. And Jon did his homework! He’s built his blog into a six-figure income.
And that’s his monthly income!
That’s right: He makes more in a month than most people earn in a year. So it’s fair to assume that he’s good at online marketing.

And, he did all of it with just the power of his voice. Jon is paralyzed from the neck down.
When he decided to make marketing strategy a key focus of his blog, he knew that sharing the lessons that he learned when building his blog and former businesses would attract a lot of readers.
But, he also knew that he could get even more fans and potential customers by teaching people how to implement the marketing strategy that he used to growth hack his companies to these huge revenues in such a short time.
Similar to Backlinko, he often breaks down a marketing tactic step-by-step with screenshots, results, and detailed how-tos.
Super specific instructions like this are rare in any industry. If you can take people by the hand from A to B, that’s when you’ll build a loyal following.
What’s more, Jon often brings on guests to share their best tactics in the same manner so that you can learn about other ways of online marketing as well, such as building relationships, Google Analytics, and email marketing.
One way to learn what it takes to create awesome content is to just look at Jon’s writing.
For example, take a look at this intro.
In it, Jon coins an entirely new term that he introduces the reader to. He alienates the audience by addressing them as “them” even though every reader knows that Jon is talking to him or her personally.
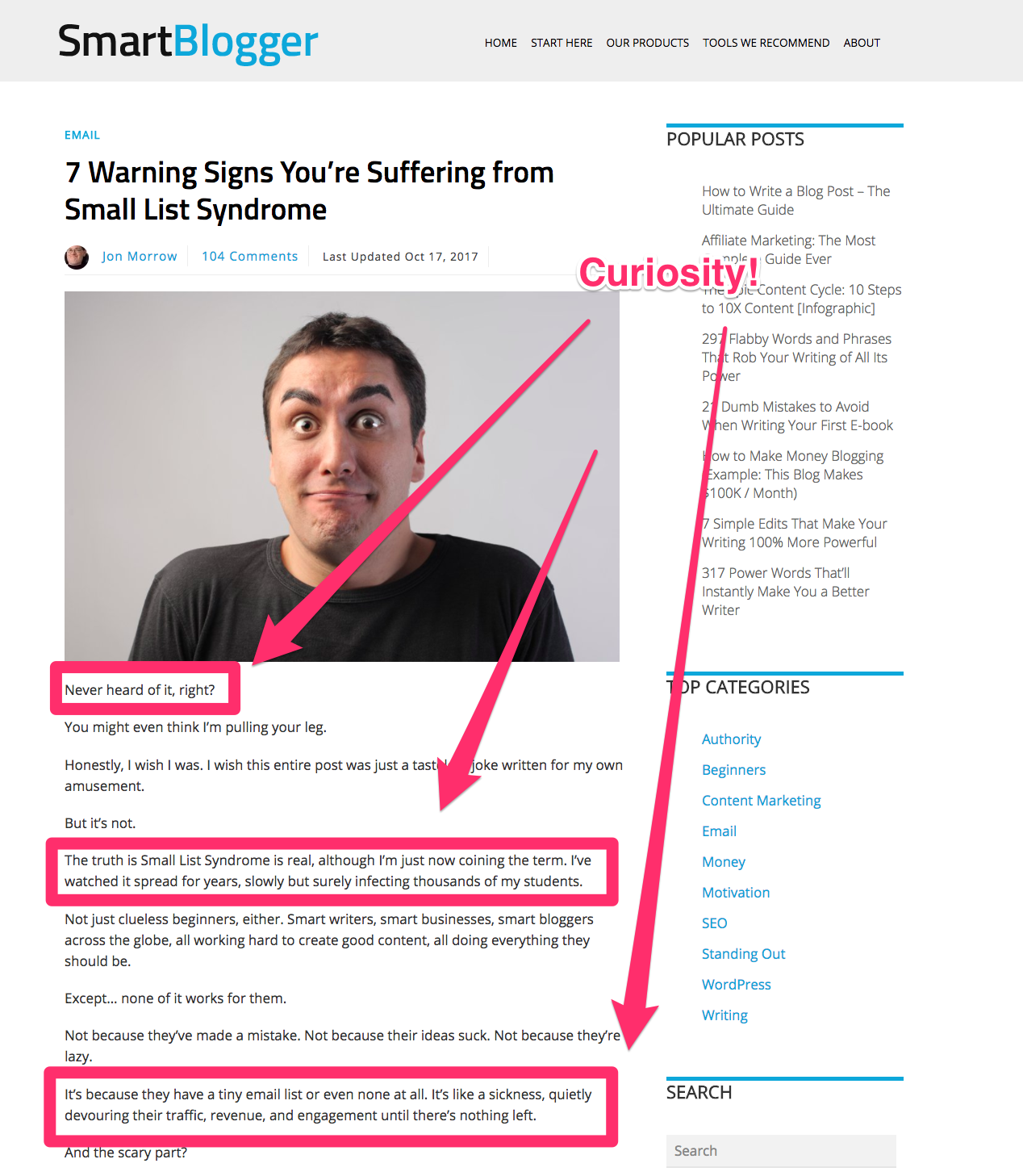
Then, he explains his terms and compares a common blogger’s problem to a sickness. Anyone would want to know how to cure it! He creates a huge curiosity gap, and he immediately draws the reader in.
Another way to learn from him is by straight up reading his content about, well, creating content. Three good articles to start with are:
- Demystifying Epic Content: How to Actually Create It (Not Just Jabber About How Important It Is)
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing Irresistible Subheads
- 20 Rules for Writing So Crystal Clear Even Your Dumbest Relative Will Understand
Why content marketing?
So, why do you need content marketing? Because content marketing is SEO.
According to Google, content is one of the top two ranking factors. The more amazing content you create, the higher the chance you have of bringing in new traffic and leads from organic search.
If you’re looking to start an SEO marketing strategy, you need to produce content. The only way that people will discover your company from organic search (from a non-branded search) is through content.
For example, if you are a law firm without a strong brand presence, you’ll need content that users are searching for to drive traffic.
You could publish an article on “Top 10 Things to Know When Getting in a Car Crash.” Blog content like this can drive inbound traffic to your website that you don’t have to pay for.
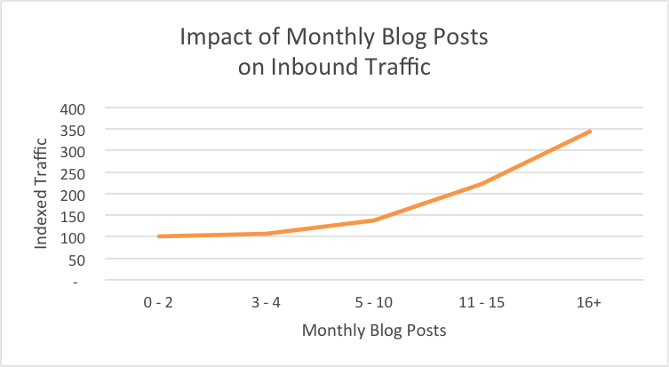
According to HubSpot, companies that post 16+ content pieces per month drive much more traffic than those that don’t:
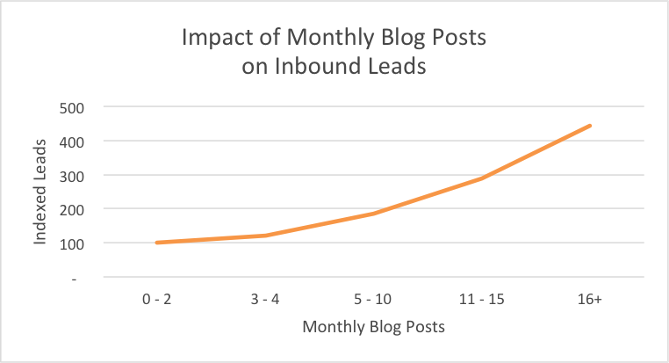
Posting 16+ times per month not only drives traffic to your website, but it also increases the number of leads you get:
The more blog-based content you have, the more indexed pages on Google you have. Combine the two, and you have a lot of chances to get someone to visit your site:
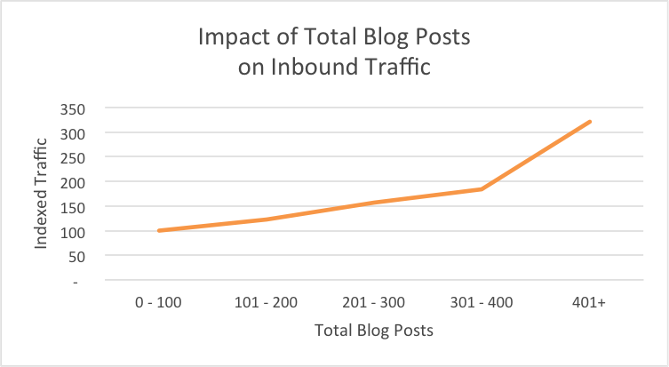
Content marketing is the key to powerful SEO.
Sure, you can optimize your product pages and your homepage. But that won’t bring in traffic that doesn’t already know you.
Content marketing is the key to bringing in new visitors who haven’t heard of you!
Plus, the ROI of content marketing is massive:
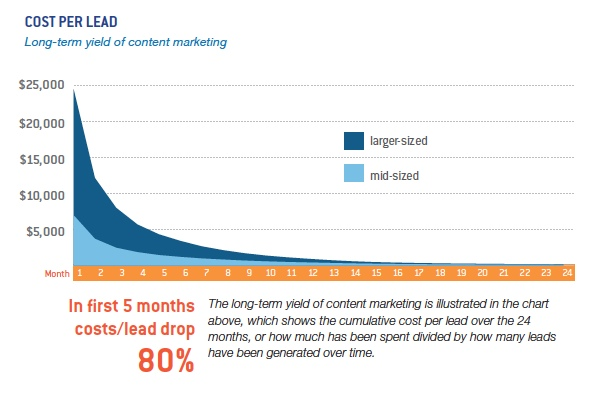
In the first few months, costs per lead can drop by 80%.
While content marketing isn’t an overnight success like PPC might be, no other tactic can match its long-term viability.
Results might take a few months, but costs are overall much cheaper than paying for customer acquisition.
HubSpot’s State of Inbound report found that marketers are still focusing heavily on growing their organic presence through blog content creation.
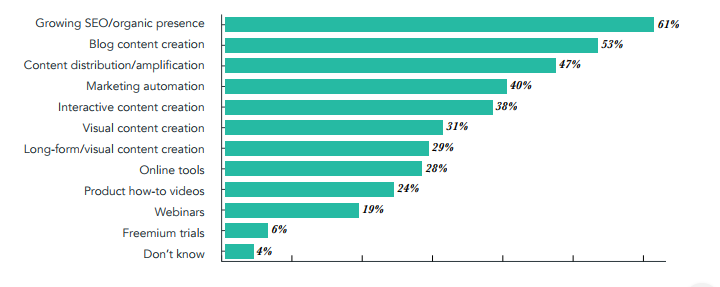
Content marketing is still the number one task for the majority of businesses trying to generate more customers and sales.
Now is the time to hop aboard the content marketing train.
But what if you don’t want to blog? Well, you don’t have to. Here are the different forms of content marketing and how you can use them to fit your own business goals.
Forms of content marketing
Content comes in many more forms than writing.
For example, Daisy Jing grew Banish, her Shopify store, to earn $3 million in annual revenue by creating informative YouTube videos about acne.
Content can come in almost any form. It includes photos, blogs, podcasts, viral videos, and more:
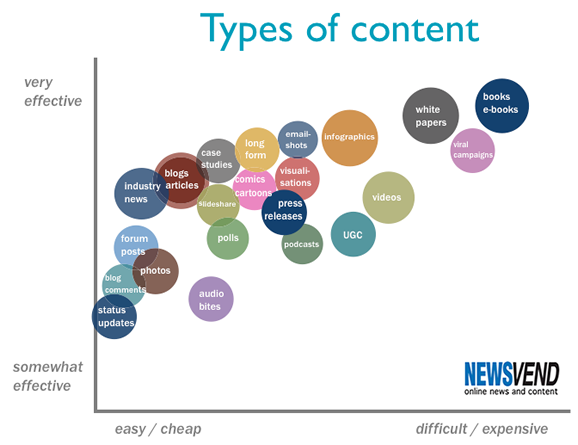
If your strength isn’t blogging or writing, or if they simply aren’t a great fit for your business model, don’t stress about it.
As long as you are creating some form of unbranded content that users need, you’ll find success.
For example, can you develop videos to upload to YouTube? I currently create videos on the top marketing struggles or trends in my niche:
These videos serve as a form of content that can help me rank on Google searches while also providing valuable content on YouTube searches.
As always, this content serves a few major purposes for my company:
- Building brand awareness: By spreading my content and my name with tons of videos, people start to recognize my brand.
- Developing credibility and social proof: Posting informative, data-rich videos shows that I am a thought leader in my space, giving me instant credibility.
- Driving traffic and sales: I produce all of my videos with ROI in mind.
But what if you don’t have the resources or time to create video-based content?
Try building a blog that focuses on photos like Pura Vida Bracelets does:
Their company sells bracelets with a charitable purpose, so blogging doesn’t really fit their niche.
Nobody wants to read about bracelets. They want photos of the bracelets and downloadable, lifestyle-based content.
Pura Vida meets these needs perfectly.
Blogging isn’t for everyone or every business. You simply need to find your content niche and start producing that content ASAP.
If you want to know more about other ways of creating content, take a look at my content marketing guide.
Content mapping by customer journey
One lingering question you may have is this:
How does content help to drive sales and bring in new customers?
Well, that answer is complicated. But the best way to summarize it is through a customer journey.
Let me explain:
When someone visits your site or interacts with your brand on social media for the first time, there is no chance that they will buy from you.
Why? Because they don’t know who you are!
Would you Google search for “shoes” and buy the first pair you saw? You probably wouldn’t.
Customers buy in a logical manner, following a specific journey from awareness to decisions. HubSpot calls this the buyer’s journey:

Customers move in progressive stages where they become aware of their problems, assess possible solutions, and then come to a decision.
This means that your content marketing efforts have to align with this journey. If you offer a user a lead magnet that requires them to give you information in the awareness stage, you’ll simply scare them off.
They don’t know your brand, so how can you expect them to give you information? You haven’t built the trust and credibility yet. The relationship isn’t there.
But if you ask for their information in the consideration stage, you’re right on track! They are brand aware and want high-value content.
Mapping your content to the customer journey means aligning your content efforts with each stage.
For example, check out this content marketing funnel:
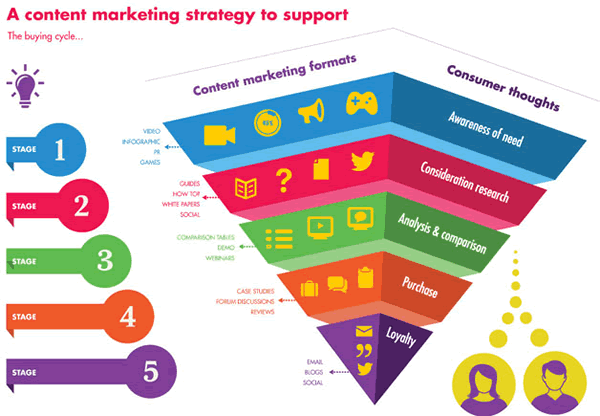
In stage one, the consumer is aware of their problem and need to fix it. This would be a great opportunity to use an infographic or an easy-to-follow video to capture attention and develop interest.
In the second stage, the user is researching their options. As they move down the funnel, content starts to get better and better.
While blog posts are great for developing awareness, they aren’t going to convert a user to purchase. They simply exist to bring users in.
Later down the line, you can push lead magnets like white papers to drive a sale.
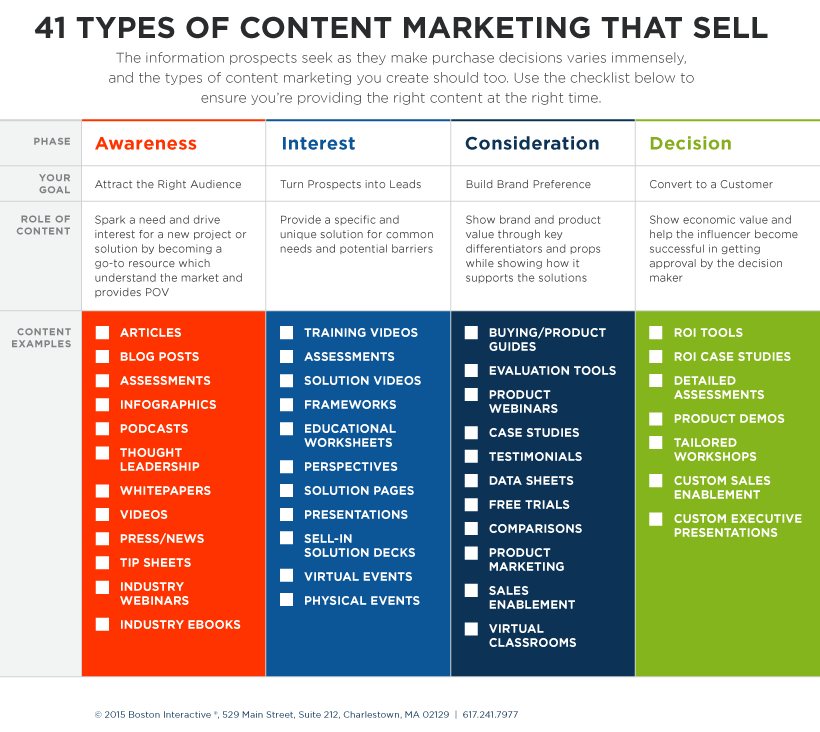
Be sure to always map your content to the buyer’s journey. If you need ideas, here is a checklist of content types for each stage of the funnel:
Content publishing and syndication
Once you’ve created content, the next step is to publish that content and syndicate it on as many platforms and sites as you can.
Content is great on its own, but it never hurts to boost it on social media or share it with other content creators.
This will help you drive more traffic and links to your content, increasing your chances of ranking and getting leads.
The most common step is to share content across social media platforms.
For example, using a tool like Buffer, you can schedule a new content piece to publish on every single social platform that your business is connected to:
I use this strategy to share every new blog post on social and to promote all of my latest pieces:

Syndication is another tactic to help expose your content to as many people as possible.
Content syndication is simply the process of publishing your content (blogs, videos, etc.) to third-party sites that will re-publish it on their own.
Do you want to syndicate your content and get more traffic? Check out my guide here:
Social media marketing
Social media is a beast. This industry is gigantic, and its growth rate is scaring even me.
By now, there are hundreds of social media networks out there.
This topic deserves a whole guide on its own, but if you want to be successful with social media (and you’ll HAVE to in the long run), your best bet for a one-stop shop is Gary Vaynerchuk.
Gary is firing on all cylinders and platforms. He has written three New York Times bestsellers (two of which solely focus on how to use social media for your business), and he runs one of the biggest media agencies around.
He’s successful on Twitter because he’s witty and engages with lots of people individually. He has managed to amass 1.64 million followers on the platform.

On YouTube, he dominates with his #askgaryvee show, which he publishes every working day of the week.
Then, there’s his Facebook page with over 2.5 million likes and his Pinterest board with nearly 20,000 followers. And, of course, he couldn’t miss out on Instagram. He’s grabbed another 2.8 million followers there.
Several million people follow his every move. If you watch him closely, you can learn the art of social media from him.
One of the biggest takeaways from Gary is that content follows context.
He says, “Content is king, but context is god.” What he means is that if you don’t respect the context of each individual social media platform, you’re bound to lose.
For example, I could have posted this blog post as a Facebook status update, but would that make any sense? No!
No one consumes long-form content on Facebook. That’s what blogs and YouTube are for.
Twitter’s video platform, Vine, was immensely popular for a time. But lots of people completely failed at building a big following on it because they were putting out the wrong content.
If you only have 6 seconds to capture the attention of your viewers, the feeling you try to excite in them had better be strong.
Only two kinds of accounts were able to pull that off consistently: Musicians and comedians.
Go through the list of the top Viners, and you’ll see that 99% of them were comedians making short, funny videos.
Instead of seeing social media as a distribution channel where you push out the content that you created on one platform to all of the others, try to tell stories that match the context of each platform.
Since Gary is also a speaker, you can learn a ton about social media by watching his talks on YouTube.
But Gary’s not the only social media wizard out there, so here are a few other resources to help you learn how to thrive on various social media platforms:
- 17 Killer Facebook Post Ideas For Small Business Owners
- 20 Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn & Pinterest Features You Didn’t Know Existed (But Totally Should)
- Instagram Marketing: Your Complete Guide to Instagram Success
- The Biggest Social Media Science Study: What 4.8 Million Tweets Say About the Best Time to Tweet
How brands are using Instagram
Instagram is becoming one of the most popular social networks in the world:
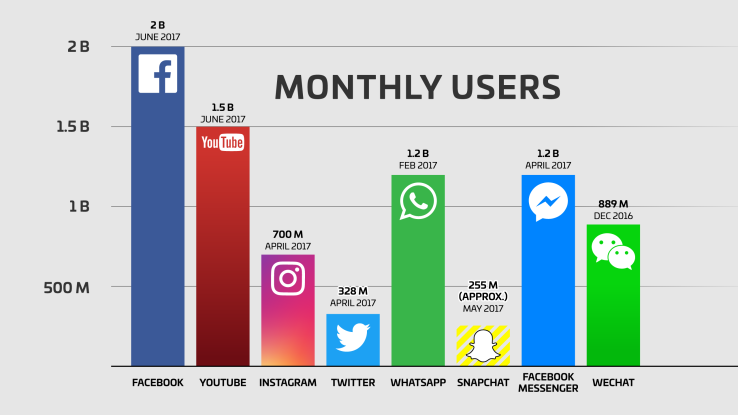
At over 700 million monthly active users, they’ve surpassed Snapchat and Twitter combined.
In just a few years, Instagram has seen incredible growth.
Brands are tapping into this growth to showcase their products and drive sales.
One of my favorite examples of brand success on Instagram is HubSpot.
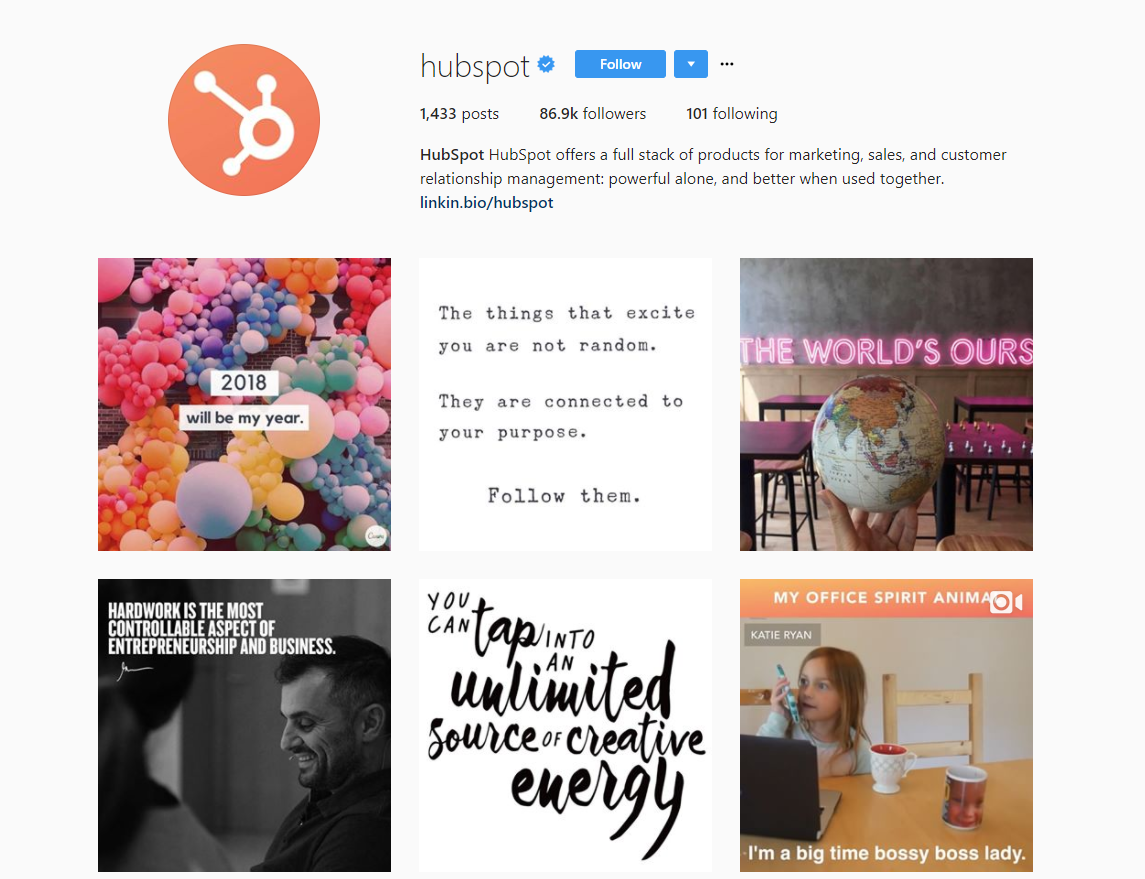
HubSpot excels at producing marketing and entrepreneur-related content for their followers.
Instagram is, of course, focused on visuals. And HubSpot taps into this by producing beautiful images and video-related content with marketing tips.
They perfectly combine inspiration with tactical tips for a great, well-rounded Instagram account.
Do you want to get started with Instagram marketing? Create an Instagram for your business and start posting content related to your niche.
If you need more tips, here are a few articles to get you going:
- Beginner’s Guide: How to Build a Killer Instagram Following and Increase Your Sales
- How to Get 300 Real, Targeted Instagram Followers Per Day
How brands are using Snapchat
Snapchat is another popular social network channel that can be huge for building brand awareness.
While it’s not as popular as Facebook or Instagram, it still works to create a following that engages with your content.
Currently, brands are finding huge success by using influencers to promote their content.
For example, Disney hired Mike Platco to post on their Snapchat account:
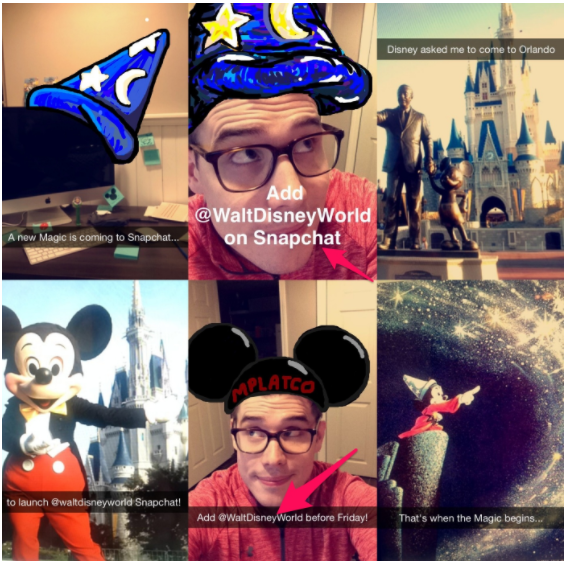
Leveraging his following, Disney was able to drive big sales and brand awareness.
Snapchat can be a great place to post behind-the-scenes content from your company like Everlane does:

Snapchat is great because the options are so diverse. You can post anything you want just like you can on Instagram.
Do you want to learn more about Snapchat marketing? Follow these tutorials:
- New Kid Alert: How to Drive Sales to Your Business Using Snapchat
- The 4 Principles of Successful Snapchat Marketing
2018 social media trends to be aware of
As consumer behavior changes and technology expands, trends will always be shifting.
Current trends show us that social media marketing is changing fast. While social platforms have always been amazing for organically reaching customers (and for free), that is slowly becoming less of a reality.
While Facebook once was the king of organic reach, it’s been declining for years now.
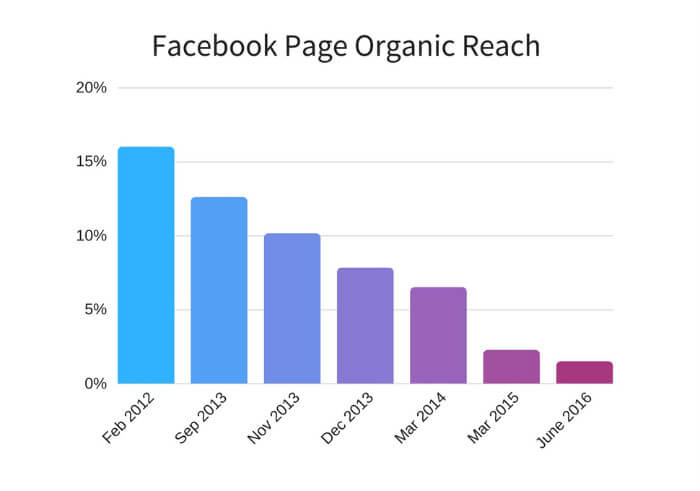
The organic reach levels are nearly at rock bottom compared to five or six years ago.
Why? The social media landscape is becoming a “pay to play” sector.
As social media platforms grow, they realize that ad revenue is their number one money maker.
And simply giving away free organic visits doesn’t help their cause.
With that in mind, you need to have a combination of both organic and paid posts on social media to find the most success in your marketing plan.
Paid social advertising
All social platforms have their own forms of paid advertising. From Instagram to Facebook to Twitter, you can sponsor posts and even create powerful custom audiences.
On Facebook, advertising works in the display format. Here’s an example of an ad that I’ve run on Facebook:
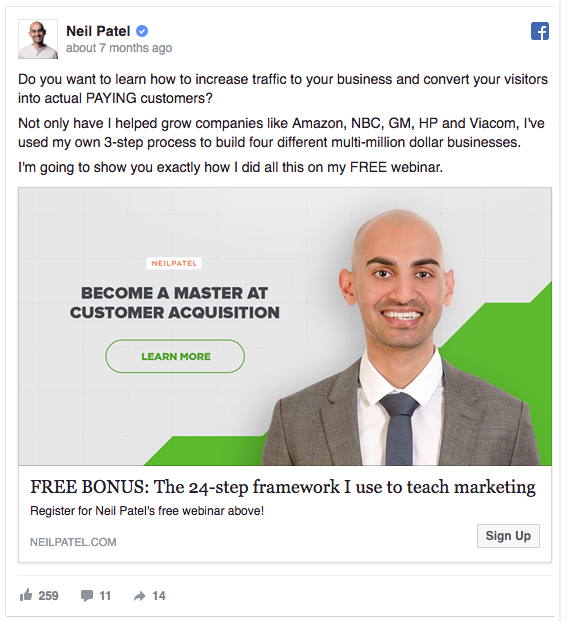
These ads show up directly in the news feed of customers you are targeting.
Facebook has some of the best audience targeting options in the market. You can effectively target audiences by income, interests, job positions, and just about anything you can think of.
Here are a few articles to get you going with Facebook advertising:
- Facebook Advertising Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Beginner’s Guide to Running Facebook Ads That Convert
On Twitter, running ads is a great way to boost your posts. I love running Twitter-based ads that boost my latest blog posts to get more traffic.
One of my favorite examples of a powerful Twitter Ad comes from Simply Measured:
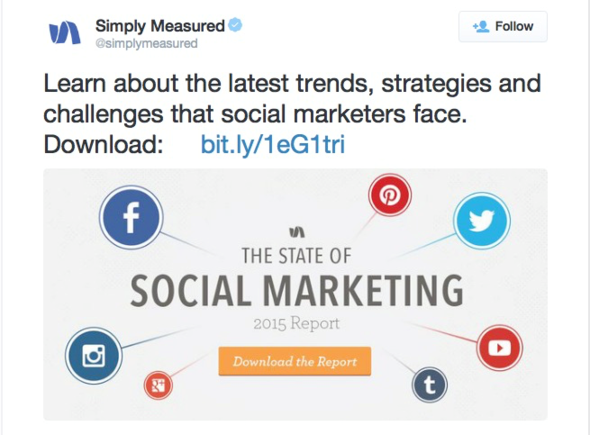
Using their content, they boost their posts to create ads for relevant, targeted audiences.
This allows them to reach a larger audience than their own following, bringing in more traffic, leads, and followers.
To get started on Twitter with advertising, I recommend reading this resource:
Lastly, LinkedIn is one of my favorite places to advertise and promote content. LinkedIn not only offers successful organic posting, but it also has a user base of high-level users.
It helps you reach people who are otherwise hard to reach, such as c-suite executives.
Content promotion and audience targeting are the keys to LinkedIn. Currently, the best ad I’ve seen on LinkedIn comes from IR:

They use LinkedIn’s lead generation ads to drive email sign-ups with compelling content. LinkedIn, just like Facebook, has diverse audience targeting options and ad options.
Get started today by following this tutorial:
Pay-per-click advertising
Pay-per-click advertising (or PPC) is exactly what the name suggests. You pay for each click that you receive on an ad that you create.
Sounds similar to search engine marketing, doesn’t it? That’s because it is. But, while SEM is only one type of PPC advertising (and a very special one), many platforms offer to show your ads to their audiences with PPC, too.
Twitter does it, LinkedIn does it, YouTube does it, and a couple of years ago, Instagram introduced ads as well.
But, by far, the most popular platforms for PPC advertising are Google AdWords and Facebook.
On Facebook, you create an ad that looks just like a Facebook status update.
Then, you can pick a specific audience. For example, you could target women in Austin, Texas between the ages of 32 and 45 who like Jon Bon Jovi. Yes, it’s that specific.
Last, you set a budget based on how much you’re willing to pay per click.
Facebook will then serve your ad to your audience in their Facebook news feeds on their desktop computers or their mobile phones.
You can also place ads in the sidebar.
When people click on your ad, Facebook will redirect them to your page, which can be part of your Facebook fan page or any URL you define.
This way, you can get people to buy your product, read your content, or, as in this example, sign up for a free webinar. Grant knows how to run Facebook Ads:
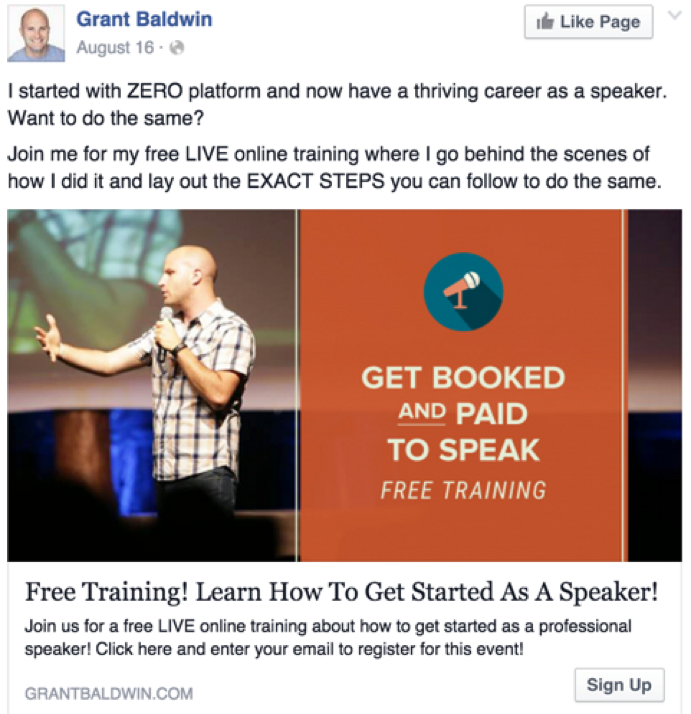
What’s good about PPC is that it integrates seamlessly into the flow of its respective social media platform.
Ever since marketers first started advertising heavily, consumers tried to avoid it.
Why?
Because in 99% of all cases, it’s not relevant to them.
What college kid needs to see a billboard about adult diapers? None!
With PPC, marketers can be sneakier. And we need to be.
The ads show up as part of the natural “just scrolling through my Facebook feed” process and are much less obvious.
Plus, thanks to the specific targeting, you can now make sure that relevant potential customers actually see your ads.
A prime online resource is AdEspresso. They offer software that layers on top of Facebook’s fairly complicated ad manager.
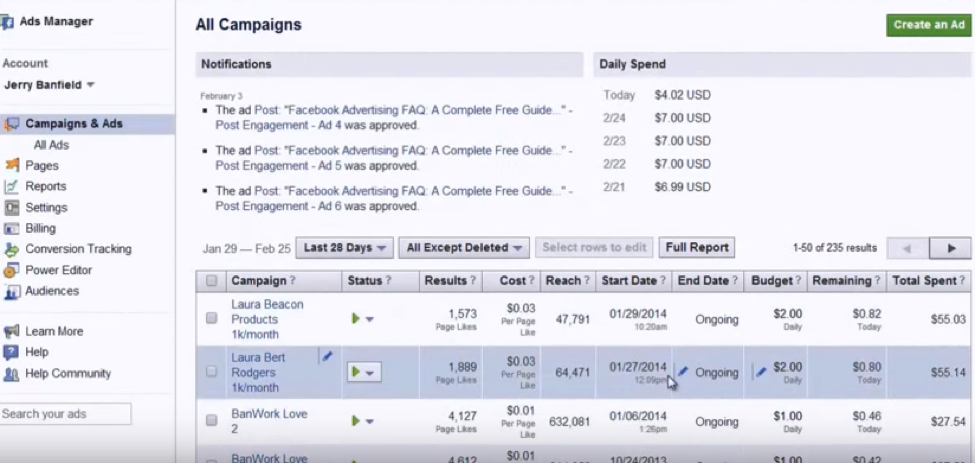
But, the blog is where they hide the good stuff. They have a guide to Facebook Ads for beginners, and it’s a great starting point.
Here are some other good articles and resources to help you start your first Facebook Ad campaign:
- What I Learned Spending $3 Million on Facebook Ads
- How to Create Facebook Ads: A Step-by-Step Guide to Advertising on Facebook
- Beginner’s Guide to Running Facebook Ads That Convert
Everything that you need to know about Google AdWords
In pay per click (PPC) advertising, Google AdWords is the most popular platform to conduct business on.
The net digital ad revenues of Google AdWords were nearly $30 billion in 2016, and they’re on track to grow to $45 billion in 2019.
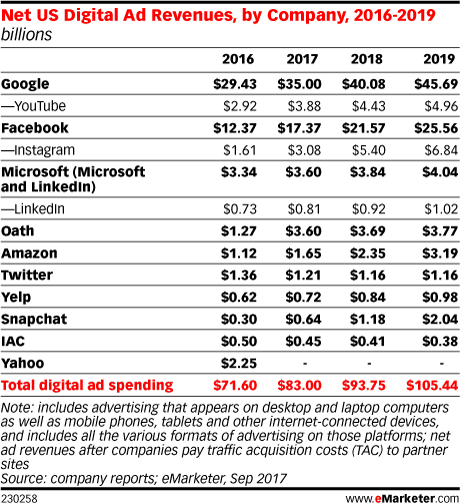
Second to Google AdWords is Facebook, but they are still behind by a large margin.
So, why does Google AdWords dominate the PPC space? It’s simply because Google is, by far, the most popular search engine in the world:
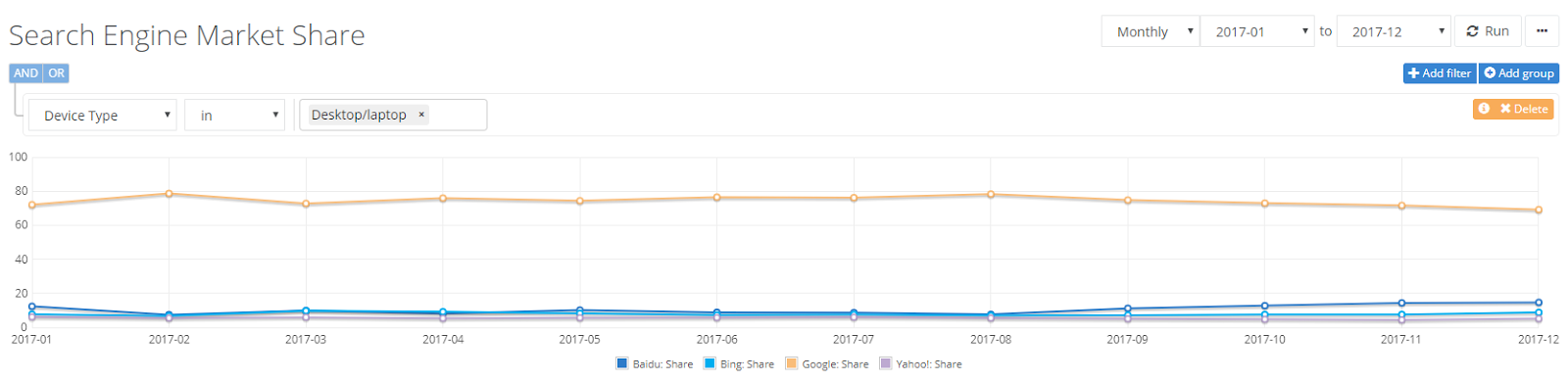
Nothing else even comes close to the power and user base of Google.
That means that everyone wants to advertise on Google to capture these billions of users daily.
Advertising on other search networks can be great, but the user bases are much smaller, making it harder to reach your target market.
With that in mind, Google AdWords is one of the best places (if not the best place) to focus your PPC strategy on.
How does it work?
Google AdWords operates on a bidding-based system. For example, on the search network, you bid on different keywords against multiple other advertisers who are looking to rank first.
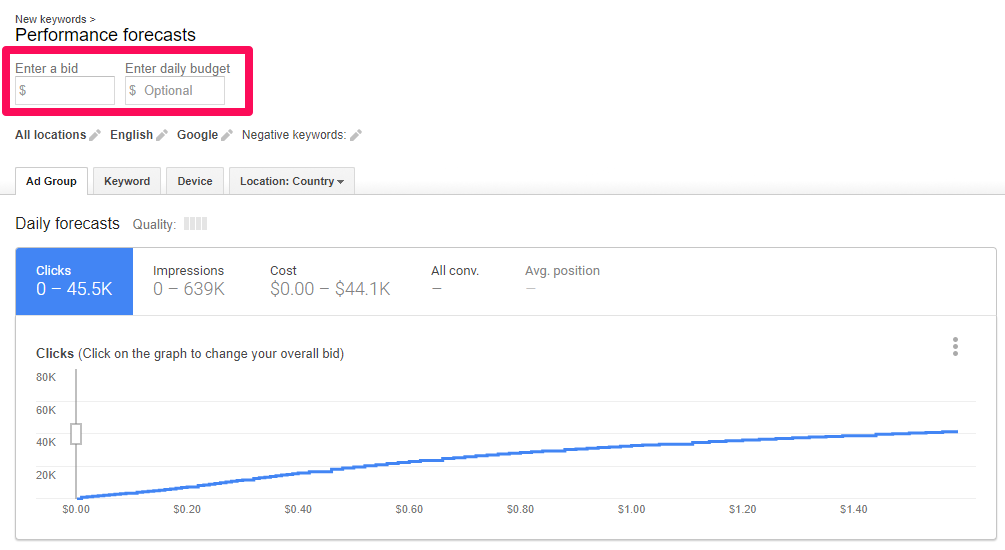
Keywords can cost anywhere from ~$1 to $500+ depending on your industry. Keywords will cost whatever advertisers are willing to pay for them.
For example, a keyword for a law firm might cost $100 per click because their end profit from a single case could be thousands of dollars. That means that they are willing to bid that high because their profits can justify it.
On the other hand, cheaper products will result in cheaper costs per click.
So, where can you advertise?
Google AdWords is made up of multiple different advertising options. Here I will detail them for you and explain what works best for most businesses:
Search network
The AdWords search network allows all advertisers to produce text-based ads targeting a specific keyword to show up in search results. For example, when you see results at the top of a search result marked “Ad,” that’s the search network:
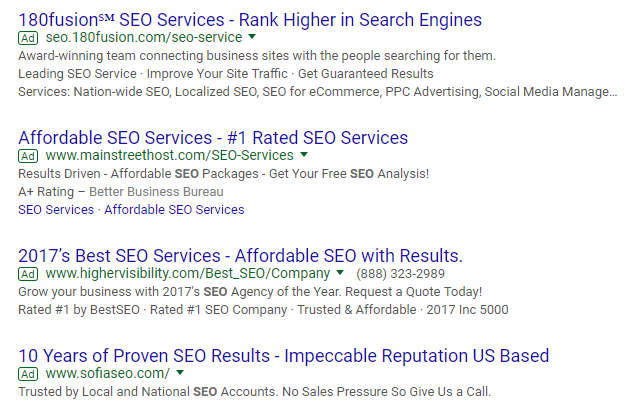
The search network is one of the most powerful PPC advertising platforms the world has ever seen.
Why? It’s due to one single factor:
User intent.
Think about it this way:
On Facebook, people aren’t browsing their news feeds to see ads, right? They are on Facebook to engage with their friends and family and maybe to see some news on the side.
But the goal of it isn’t to find products or services. It’s social media. It’s about interaction.
But the search network on AdWords is a whole different animal. People are literally searching for things based on specific keywords to find solutions.
For example, think about a search for “plumber near me.” What does that keyword signify?
That user is trying to find plumbing services ASAP.
That’s intent to buy directly from a single search. Where platforms like Facebook can take multiple ads and remarketing campaigns to convert a prospect, the search network can convert someone from a single keyword search.
It’s one of the main reasons why people love advertising on Google’s search network.
Display network
The display network is another powerhouse of advertising that Google offers to every advertiser on their platform.
The display network taps into Google-approved sites, allowing advertisers to show image-based advertisements on related sites by topic and keyword context.
For example, ads like these are from the display network:

These ads will show up on related sites or sites that you frequently browse that use AdSense.
AdSense is sort of the reverse of the display network. Rather than spending money to display ads on Google, AdSense allows publishers (sites) to make money by displaying ads on their sites.
To clear it up:
Display advertising is PPC advertising where you create image-based ads and pay for each click.
AdSense is the opposite end where websites can allow Google to show those display ads on their sites to make money.
Here is an example of display ads at work:
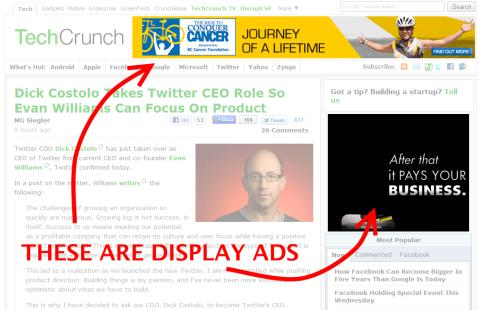
They’re often sitting above the website or on the sides of the web page, and they’re a great way to capture new users.
On top of that, the display network offers another powerful feature:
Remarketing
Remarketing is the process of bringing back users who have previously engaged with your company.
If you have remarketing enabled, you could use ads to target users who landed on your website but didn’t convert.
This allows you to bring those users back for a second or third or fourth shot at buying from you.
And you need remarketing because about 96% of your visitors aren’t yet ready to buy from you.
One of my favorite examples of a powerful remarketing ad on the display network is from Blue Corona:
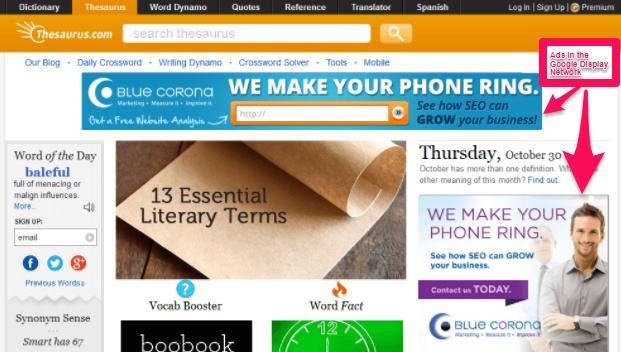
Visiting their website and exploring their services leads them to target me with a few different ads about SEO.
It helps reinforce their brand and hopefully get me to click back to their site and convert me this time around.
The Google AdWords display network is great for remarketing, and anyone can set it up.
Google AdWords is the largest and one of the best PPC networks you can use.
Do you want to get started on it today? Here are a few key resources for you:
- Google AdWords Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Entrepreneur’s Guide to Google AdWords
- I Increased Sales When I Made this One Google AdWords Change
- Unbelievably Devastating Mistakes People Make with Google Adwords
Read those posts, and you will be on your way to dominating Google AdWords and driving sales like you’ve never imagined.
Affiliate marketing
You can’t spell affiliate marketing without Pat Flynn. Well, you actually can, but you shouldn’t learn it without him.
When Pat created Smart Passive Income in 2008, he was just starting to get familiar with selling informational products online. His first product was Green Exam Academy. It’s a course that he created to help people pass the LEEDs exam for architects, and it sold well.
He wanted to learn more about the concept of passive income, which is where you earn money without actively working for it (after an insane amount of work up-front, of course).
Given his most recent income report, let’s just say he managed to learn quite a bit:
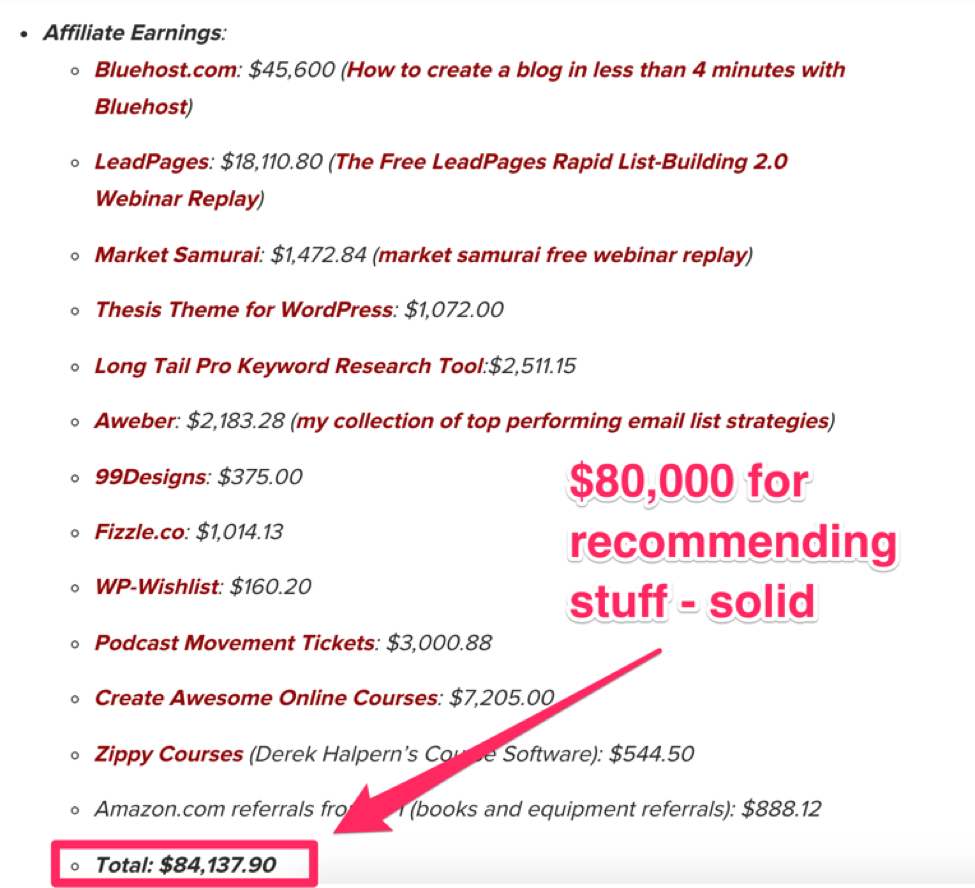
Affiliate marketing is his single biggest source of income.
But, what exactly is affiliate marketing?
Imagine that you know a great pizza place. You know the owner, Luigi, and you go there all the time.
Naturally, you tell your friends about it.
When your friend Tim goes to the pizza place, he mentions that you told him about the pizza parlor and proceeds to buy four pizzas for his friends.
The next time you come back, Luigi says, “Dude, your friend bought four pizzas because of you, and that’s the biggest order I had all week! Thanks, man! Here’s $5 for referring him.”
Ka-ching!
You’ve just made your first affiliate marketing sale.
Except, it doesn’t usually happen in real life like this, especially because a pizza place whose biggest order in a week is four pizzas won’t be around for very long.
But luckily for you, there’s a place where it happens all the time: Online.
Amazon is a prime example (pun intended).
When you sign up for their affiliate program, you can generate a special link for every single product page that they have.
You can then put that link on your blog, for example, or send it to friends who you want to recommend that product to. If they click your link and buy the product, you’ll get a small commission from Amazon for referring that customer.
Over the last seven years, Pat has built the best resource online about affiliate marketing. Some great starting points are:
- Welcome to Smart Passive Income
- 3 Types of Affiliate Marketing Explained—and The One I Profit From
- 8 Principles for Effective Affiliate Marketing on a Blog
How to get paid in affiliate marketing
Now that you have a basic understanding of how affiliate marketing works, how do you get paid?
As I explained in the pizza example, you usually get paid every time your referral leads to a sale.
One of the most popular ways to drive affiliate sales and get paid is by blogging or creating content around those products.
NerdWallet is a great example of a business that thrives off of affiliate marketing:
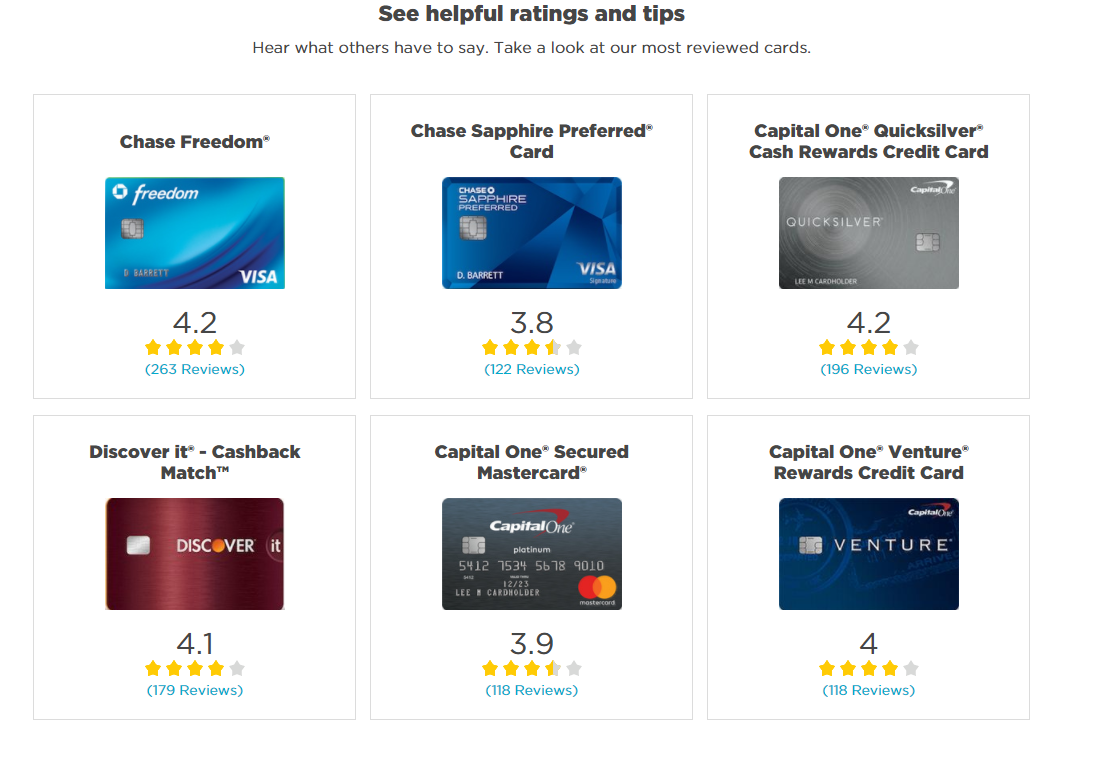
They focus on personal finance, so they review different credit cards and help users find the best cards for their businesses or lifestyles.
But here’s the kicker: they make money every time someone signs up for a credit card using their site.
For example, if someone clicks on “Chase Freedom” card and signs up, NerdWallet gets a portion of the revenue for their efforts.
Do you want to take your affiliate marketing to the next level? Follow this guide to add affiliate marketing to your online marketing game plan today:
Email marketing
I want to introduce you to your new best friend when it comes to learning email marketing.
Meet Bryan Harris, founder of Videofruit.
Think about those days where you keep complaining all day long until you see your best friend and she immediately says, “Shut up, stop complaining, and do this instead!”
That friend is Bryan.
In the past two years, he bootstrapped his blog from $0 to a six-figure business. His latest course made a cool $220,750.
Originally providing freelance work for big brands like HubSpot and our very own Kissmetrics, he eventually started focusing more on teaching.
He says that the single greatest asset in his business is his email list.
In 2014, he grew his own list from 0 subscribers to over 10,000. By now, he has more than doubled that number.
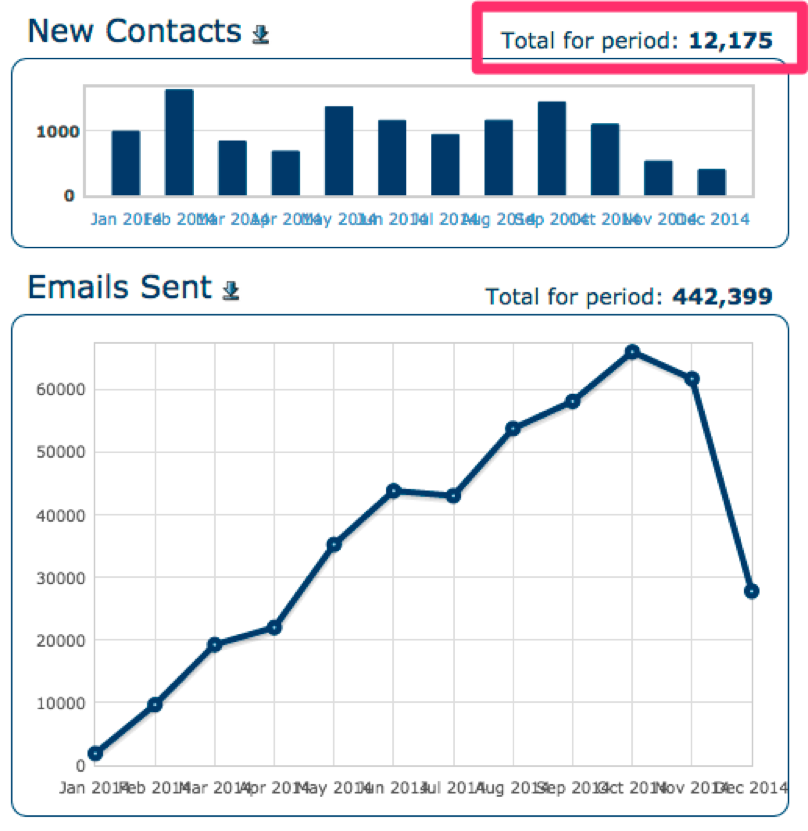
Lots of articles online show you “how to write better emails” or “how to pitch anything.” But, before you can send those emails, you first need the list of people to send them to.
That’s what email marketing is all about: Directly communicating with your audience and customers.
Email trumps lots of social media platforms when it comes to engagement. In fact, you’re 40 times more likely to gain a new customer through email than through Facebook or Twitter.
Plus, email is a good, long-term method of contacting prospects.
Think back to the last time you changed your phone number. It probably wasn’t that long ago, right?
Now, do you remember the last time that you changed your email? You probably don’t.
Changing your email is an absolute pain, so people rarely change them. That makes an email address a valuable piece of contact information to have.
Bryan is not the only one who escaped from the cubicle by building an email list, but he’s the best when it comes to teaching you how to do so.
He has a full-fledged course called “Get 10,000 Subscribers.” But for starters, check out these three posts:
- How we started an email list from scratch and got 205 subscribers in 48 hours
- Download 11 Killer Lead Magnet Ideas & Templates
- How to use a giveaway to get 2,239 email subscribers in 10 days
2018 email marketing trends
Email marketing has evolved over time, but it continues to be one of the efforts that yields the highest ROI for online marketing.
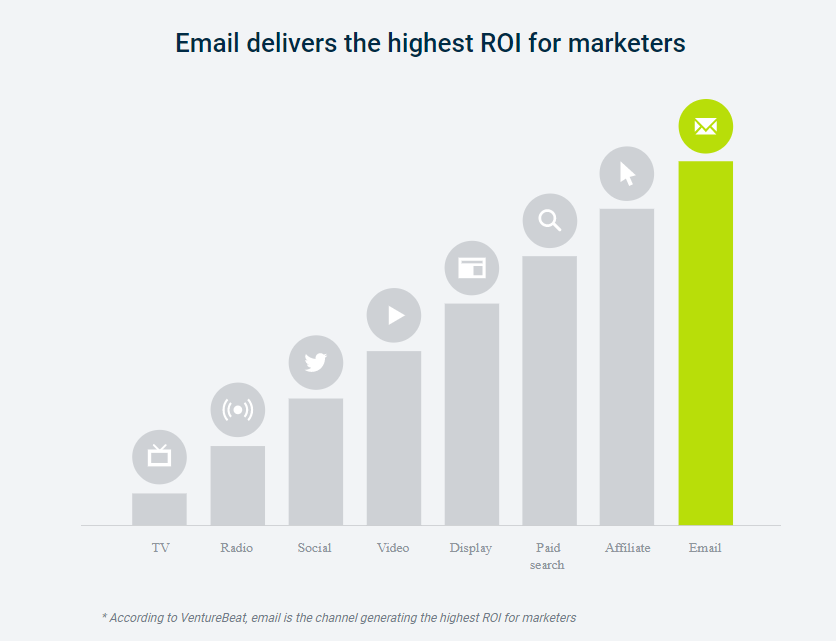
Email marketing is critical for any business to develop loyal customers and drive sales without spending a dime on advertising.
The current outlook on email marketing in 2018 trends on two specific topics:
- Personalization
- Segmentation
Personalization is one of the biggest factors for a successful email marketing campaign.
For example, check out this amazing, personalized email from JetBlue:

You need to personalize emails in the modern day. That means everything from using the customer’s name to referencing their history or interests.
Personalized emails deliver much higher open and conversion rates when you compare them to boring, templated emails:
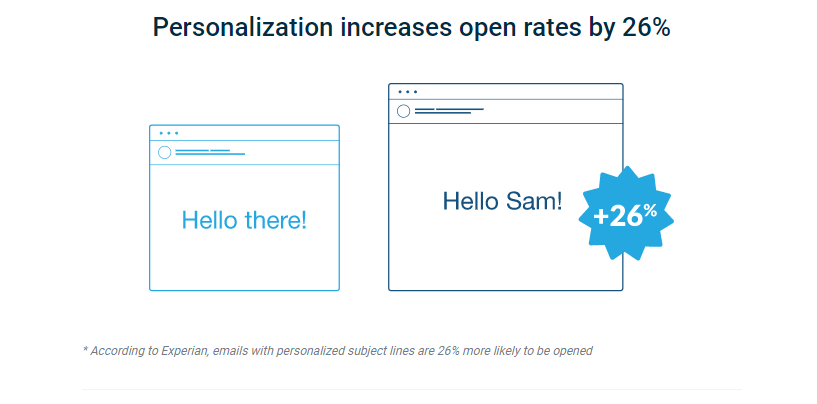
Writing better, personalized emails is a great way to boost your online marketing efforts.
Here’s a guide I recently wrote about personalization tips. Use these in your next email campaign to see open rates increase dramatically:
A second popular trend for 2018 in the email marketing sector is segmentation. According to the latest data, segmentation can increase revenue from campaigns by 760%.
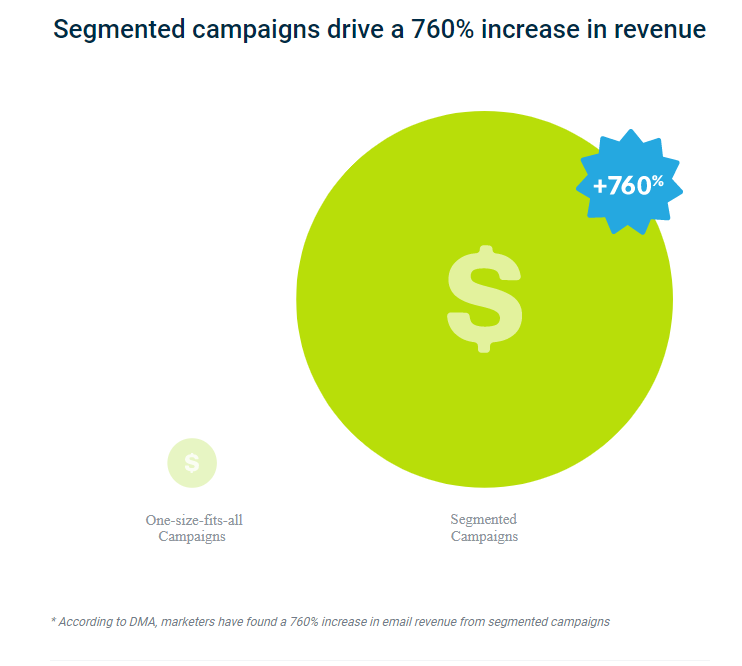
So, what exactly is segmentation?
Segmentation focuses on splitting up your customer email list into specific groups, allowing you to target them with much more specific content.
For example, let’s say that you have customers who have purchased basketball shoes and customers who have purchased soccer shoes.
Sending a generic email about a coupon likely won’t generate sales. But splitting those groups into two email lists and sending specific basketball and soccer shoe coupons will skyrocket engagement.
For example, look at this email from Bryan Harris who was looking to validate his online course. To do this, he segmented his email list for users who downloaded content that was similar to his online course:
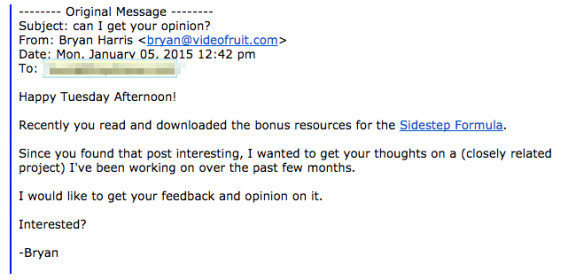
This customized, segmented email blast generated a 72% reply rate.
Making email marketing as specific as possible is going to help you drive better open rates, response rates, and conversions.
Do you want to learn more? Here’s How to Use Email Segmentation to Increase Your Conversion Rate.
The best email marketing tools
No good email marketing campaign is complete without a proper set of tools.
Sending emails directly from your client, like Gmail, severely limits your ability to both scale and customize.
Sure, it allows you to build lists, but it doesn’t offer personalization tools or ways to schedule out emails and drip campaigns.
A good email marketing tool can help you automate your efforts and consolidate your tools into one, saving time and money while improving productivity.
The most popular email marketing tool on the planet right now is MailChimp.
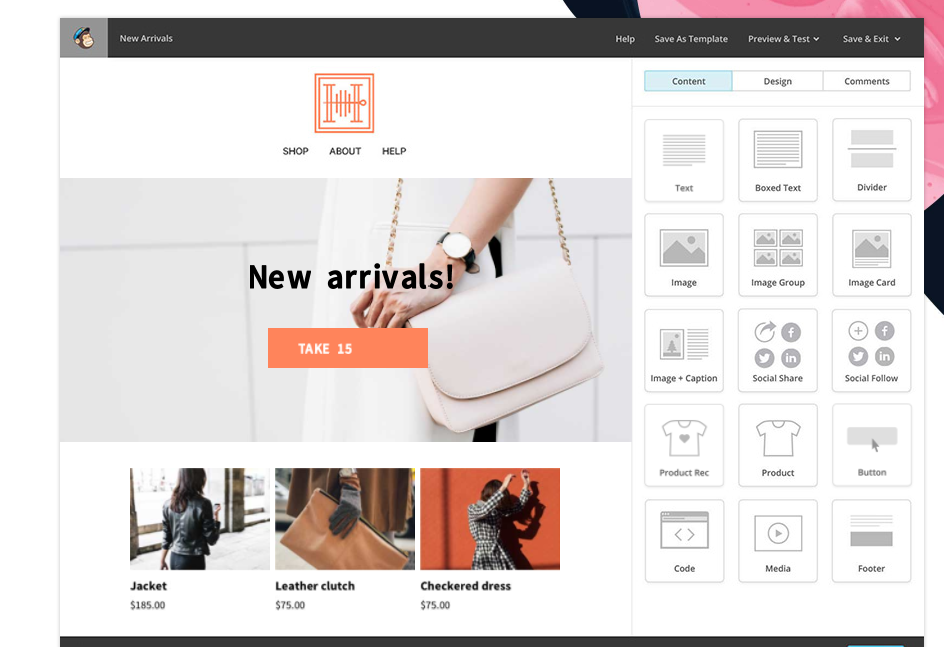
Their drag-and-drop builder allows you to create stunning email templates for any type of business.
You can do everything from scheduling email campaigns to automating, segmenting, and personalizing them, and more.
It’s safe to say that MailChimp is a one-stop-shop email marketing tool that can help your business save time.
Other amazing email marketing tools include Constant Contact, Drip, ConvertKit, AWeber, GetResponse, and ActiveCampaign.
Start with drip campaigns
Drip email campaigns are the bread and butter of a successful email marketing gameplan.
Drip campaigns are simply automated email campaigns that send follow-up emails to users who don’t respond.
For example, if a user doesn’t respond to email #1 about your offer, you can re-engage them with a second, automated email in two days to remind them.
Similar to remarketing, they offer another chance for a user to convert.
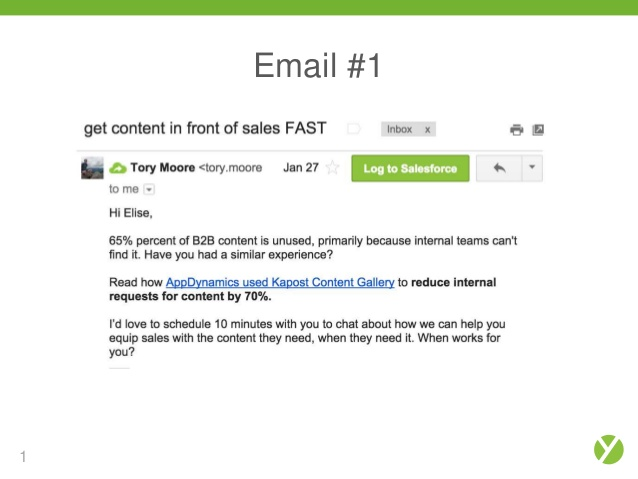
One of my favorite examples of a drip campaign comes from Kapost. Here is the first email in their sequence:
Later down the line, when the prospect isn’t responding, Kapost taps into personalization to re-engage the user:
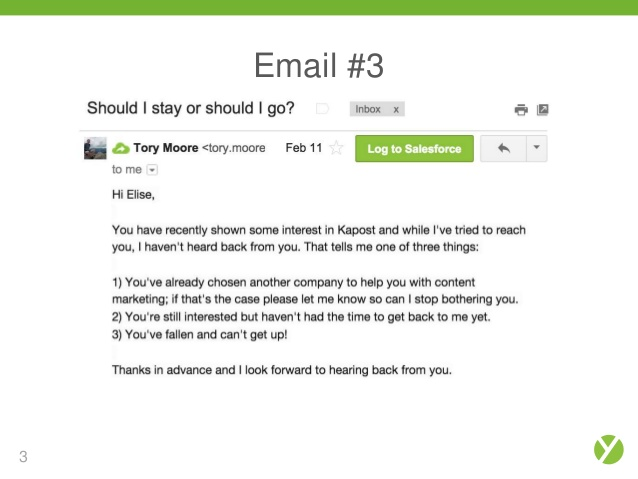
By referencing their interest in Kapost’s content, they are showing a deep level of understanding for the customer.
Drip campaigns should be a big part of your online email marketing efforts.
Get started creating a powerful drip campaign today with this Quick Sprout guide:
Conclusion
Online marketing is the real deal. Of course, guys like Chandler are the exception. But thanks to the power of the Internet, anyone and everyone can become financially independent through Internet marketing.
You can ditch the boss, the nine to five, and the fear of losing your job.
But, that’s easy to say. It’s far harder to do. If you do anything right, it’s hard.
Online marketing is no different. To get ahead, you need to get started.
I hope this guide will help you do just that.
What’s your favorite type of online marketing? Are you building a business with it? Which type of marketing will you learn next? Let me know in the comments!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Online Marketing?
Online marketing is the practice of digital channels to spread your message about your products or services. Some of the ways you can do this are through paid ads, social media, emails, blogging or even SEO.
What does an online marketer do?
An online marketer drives traffic a website in order to help a company generate more leads or sales. This can be done through a variety of channels, such as emails, paid ads, SEO, social media, or even content marketing.
How do you learn online marketing?
The easiest way to learn online marketing is to setup your own site, such as a WordPress blog, and then practice writing content and promoting it. From there you can get into more advanced forms of online marketing.
Is online marketing expensive?
With online marketing you can either go after free traffic sources or paid traffic sources. With free ones, you just have to put in time. With paid ones, they cost a fee. You can typically optimize your site to make paid sources profitable.